Posted 18 September 2015 - 02:30 PM
flashman7870, on 27 August 2015 - 03:41 AM, said:
is there ever ANY mention or allusion of the Hebrews in the book?
Othar, on 27 August 2015 - 06:20 PM, said:
Not with that name, but IMO "missionary priests of Sidon" (Sion?) could come close.
flashman7870, on 27 August 2015 - 09:53 PM, said:
Interesting idea, but that would place the origin of Judaism in Phoenecia, which considering the lack of mythological similarities between Phoenician and Jewish religion beyond those names found across the Semitic world, that seems unlikely.
kmt_sesh, on 12 September 2015 - 05:35 AM, said:
As for the Phoenicians, [...] They were decidedly Semitic, of Canaanite stock. Their own abjad (a consonantal alphabet) demonstrates this.
Some relevant OLB quotes concerning the Phoenicians.
1. Fonísjar priests = Gola = Sídon priests
1. Fonísjar priests = Gola = Sídon priests
(* I give the page number of Sandbach, but the translations here are (adapted) by me)
[200/17] (Sandbach* p.241)
ALLERWÉIKES HÀVON HJA THA FONÍSJAR PRESTERA. THAT HÉTH. THA GOLA VRJÁGETH
everywhere they have driven away the Fonísjar priests, that is, the Gola
[060/23] (Sandbach p.85)
THA GOLA. ALSA HÉTON. THA SÀNDALINGA.PRESTERA SÍDON.IS
the Gola, as the missionary priests of Sídon were called
2. About the relations between the Fryas and the Gola/ 'Fonísjar' (or: how the Fryas felt about them) - Note these are only a few examples of many more
[061/11] (Sandbach p.87)
WAS THÉR HWA FON VS FOLK THÉR.ET ALSA ÀRG VRBRUD HÉDE THAT SIN LIF IN FRÉSE KÉM
THAN LÉNADON THA GOLA HIM HUL ÀND SKUL ÀND FORADON HIM NÉI PHONISJA. THÀT IS PALM.LAND
If any of our folk had messed up so badly that his life came in fear,
the Gola lent him refuge and took him to Phonisja, that is Palmland.
[097/04] (Sandbach p.135)
THÉR KÉMOM THRÉ FONÍSJAR SKIP.LJUDA THÉR HJA WRÉVELA WILDE
three Fonísjar sailors came, who wanted to abuse them [the children]
[161/17] (Sandbach p.219)
THJU TÁLE THÉRA KÀLTANA.FOLGAR IS THRVCH THA SMÛGRIGE GOLA VRDERVEN
the language of the Kàlta-followers was corrupted by the creepy Gola
[199/30] (Sandbach p.241)
THA FHONÍSJAR SEND EN BASTRED FOLK. HJA SEND FON FRYA.S BLOD.
ÀND FON FINDA.S BLOD ÀND FON LYDA HIS BLOD
the Fhonísjar are a bastardised folk; they are of Frya's blood,
of Finda's blood and of Lyda's blood
[201/24] (Sandbach p.243)
ÀFTER NÉI NAM.ER TWÁ É.LANDA TO BERCH FÁR SINUM SKÉPUM.
ÀND HWÁNATH HI LÉTER ÛTGVNG VMB ALLE FONÍSJAR SKÉPA ÀND STÉDA TO BIRÁWANE THÉR.I BIGÁNA KV
After that, he [Áskar] took two islands to park his ships,
from where he later went out to plunder all the Fonísjar ships and cities that he could reach.
[200/17] (Sandbach* p.241)
ALLERWÉIKES HÀVON HJA THA FONÍSJAR PRESTERA. THAT HÉTH. THA GOLA VRJÁGETH
everywhere they have driven away the Fonísjar priests, that is, the Gola
[060/23] (Sandbach p.85)
THA GOLA. ALSA HÉTON. THA SÀNDALINGA.PRESTERA SÍDON.IS
the Gola, as the missionary priests of Sídon were called
2. About the relations between the Fryas and the Gola/ 'Fonísjar' (or: how the Fryas felt about them) - Note these are only a few examples of many more
[061/11] (Sandbach p.87)
WAS THÉR HWA FON VS FOLK THÉR.ET ALSA ÀRG VRBRUD HÉDE THAT SIN LIF IN FRÉSE KÉM
THAN LÉNADON THA GOLA HIM HUL ÀND SKUL ÀND FORADON HIM NÉI PHONISJA. THÀT IS PALM.LAND
If any of our folk had messed up so badly that his life came in fear,
the Gola lent him refuge and took him to Phonisja, that is Palmland.
[097/04] (Sandbach p.135)
THÉR KÉMOM THRÉ FONÍSJAR SKIP.LJUDA THÉR HJA WRÉVELA WILDE
three Fonísjar sailors came, who wanted to abuse them [the children]
[161/17] (Sandbach p.219)
THJU TÁLE THÉRA KÀLTANA.FOLGAR IS THRVCH THA SMÛGRIGE GOLA VRDERVEN
the language of the Kàlta-followers was corrupted by the creepy Gola
[199/30] (Sandbach p.241)
THA FHONÍSJAR SEND EN BASTRED FOLK. HJA SEND FON FRYA.S BLOD.
ÀND FON FINDA.S BLOD ÀND FON LYDA HIS BLOD
the Fhonísjar are a bastardised folk; they are of Frya's blood,
of Finda's blood and of Lyda's blood
[201/24] (Sandbach p.243)
ÀFTER NÉI NAM.ER TWÁ É.LANDA TO BERCH FÁR SINUM SKÉPUM.
ÀND HWÁNATH HI LÉTER ÛTGVNG VMB ALLE FONÍSJAR SKÉPA ÀND STÉDA TO BIRÁWANE THÉR.I BIGÁNA KV
After that, he [Áskar] took two islands to park his ships,
from where he later went out to plunder all the Fonísjar ships and cities that he could reach.
 |
| source |
Posted 19 September 2015 - 07:38 AM
kmt_sesh, on 19 September 2015 - 05:45 AM, said:
Better would be to use the term proto-Frisians, as they are suggested to have been a people from which the Frisians descend (and the Germans, the Dutch, etc. - NW-Europeans). Obviously, the NW-Europeans will not exclusively descend from these 'Fryas', as there have been other influences.I know very little about the Oera Linda Book, but is it not primarily about the adventures of ancient Frisians? [...] I'm confused because, despite the tales told in the OLB, the Frisians were and are a Germanic people. They did not exist in the Early Bronze Age (c. 2200 BCE), unless you all are referring to very ancient northern Europeans whose identity, language, and culture are largely lost to us now. But technically speaking, culturally and linguistically, the Frisians could not be the same people.
Although there are no (other) written sources for this, the ancestors of the NW-Europeans will have existed in the Early bronze age. Technically speaking (culturally and linguistically), the NW-Europeans could have descended from the people described in the OLB. There is nothing in the OLB (or anywhere else, as far as we have seen in this thread) that makes this hypothesis impossible.
Quote
This term is derived from the OLB itself. If it is authentic, it seems like the Nordic-Germanic traditions that have Freya as a goddess are of later date. OLB describes/ suggests several other cults that were started by priesthoods, based on deified mortals (a.o. Minerva, Wodin, Neptune, Vesta).You use the term "Fryas." Is this not a derivation of the ancient Norse goddess, or is it in reference to something or someone else?
Frya would have been the last 'Folk mother' (sort of chosen queen) from before a deluge, but the 'records' about this are more of a mythological nature. OLB also has a creation myth in which "Frya" is one of three primal mothers, namely the one of which the white race would have descended.
The name means "Free one" or "to set free", so it could also be that the people who strongly identified with the concept of freedom, created this myth of their primal mother for themselves.
Posted 24 September 2015 - 07:19 PM
Simply because it is so beautiful, and in the collection of the
Westfrisian Archive (Hoorn), where I spent too many hours of my
adolescence: Map of the world (1657) by Frederik de Wit.
Posted 28 September 2015 - 12:32 PM
I subtitled an old Dutch short film with many JOL symbols (6 spoke wheel). In the video it is called "six-star". => Separate post here.
Posted 02 October 2015 - 01:09 PM
Depiction of Friso by Pieter van den Berge, printed in H. Soeteboom, Oud-heden van Zaan-land, Stavoren, Vronen en Waterland (1702):Depiction of Friso, Adel and "Asinga Ascon" ("Áskar" in OLB) by Simon Frisius, printed in Winsemius, P.W., Chronique ofte Historische geschiedenisse van Vrieslant (1622):
It is telling that the sources from which these illustrations were taken are hardly studied, referred to or even accessible (they are not even transcribed yet) in the Netherlands.
Posted 05 October 2015 - 05:07 PM
Othar, on 02 October 2015 - 04:02 PM, said:
I am transliterating parts of this book on my blog. As far as I know this was not done before. It contains some very relevant information. I will post some of that here.Winsemius, P.W., Chronique ofte Historische geschiedenisse van Vrieslant (1622)
On page (Fol.) 6:
Joachim Hoppers (1523-1576) was a Frisian lawyer and professor who worked for the Spanish king (Philip II). He appears to have written about Frisia's ancient history, but I have not found that text yet. According to the "Chronique", he wrote that the Frisians stem from the "High-Nordic peoples or Hyperboreans" and were the first to have received the secrets of writing.Ioachimus Hopperus een licht/ ende eere onser natie/ in tijden Secretaris des Coninklijcke Majesteyts van Spangien in zijn Tafel der Coningen van Vrieslant/ deduceert die Vriesen uyt die hoogh-Noordtsche volckeren ofte Hyperboreis, van welcke hy meent dat sy d'eerste secreten ende gheheymenissen der letteren souden hebben becomen.
Another relevant fragment on p.7:
And on p.11-12:Maer dese principalijcken vinden wy in onse Landts-Historie beschreven/ dat lange na die dominatie/ ende Heerschappije der Sueven in Vrieslant uyt seeckere Provincie van neder Indien (ghelijck als d'Chronique is sprekende) geheten benedicta Fresia by maniere van Lottinge/ zynde d'selve in die tyden een gemeyne ghebruyck der volckeren/ uytgegaen zijn/ met een groote menichte drie ghebroederen met namen FRISO SAXO, ende BRUNO die welcke in d'Oorlogen des grooten Alexandri sich begevende/ aen die Emodische Geberchten [Himalayas] hunne garnisoenen ghehouden hebben.
In other words: When Friso died, he left his travelling journal, contracts, his covenant with various German cities,documents about the division of Friesland, among other things. When his son Adel succeeded him, he was said to have improved some of the written laws. Winsemius (1586-1644) adds a note saying that this is questionable, as Tacitus suggested that the Germanic tribes didn't read and write.Doch Friso overleden zijnde (wien sy schrijven gemaeckt ende naghelaten te hebben/ zijn reysboeck/ die contracte/ en 'tverbondt met die Stenden van Duytslant/ die deylinge van Vrieslant ende andere saecken) is in zijn plaetse ghevolger Adel zijne oudtste zoone/ een Prince van milden natuyre/ ende goede zeden/ die welcke die wetten die by zijn Vader tot die regeeringe/ ende proufijt der ondersaten gemaeckt waren/ niet alleen heeft toghestemmet ende voor goedt ghehouden/ maer oock d'selve met nieuwe additien/ ende toedaeningen versien/ ende int gheschrifte (alhoewel het seer te twijffelen staet om dat Tacitus lange daer na die wetenschap der letteren die Duytschen ontneemt) verbetert.
This book was published in 1622, in the early years of the most terrible Thirty Years' War (1618-1648), in which also the Dutch Republic took part. It is obvious that the book partly was of political (propagandistic) importance, specially since it was licensed by, and dedicated to the government. Still, much can be learnt from it.
Posted 06 October 2015 - 06:51 AM
Van Gorp, on 05 October 2015 - 08:12 PM, said:
Great associations VG, and plezant that you are back.I think the right side to use is the one most people prefer to use when reaching out in the dark: the test-er.
I can add this one: vin-geren = vin(d) - (be)geren
The Puzzler, on 06 October 2015 - 05:31 AM, said:
These don't have to come from Latin.... rather than Latin, which test, testi and all the textile words come from.
Latin is a relatively new (writing) language, only overrepresented in our (relatively) old texts.
Posted 17 October 2015 - 06:25 PM
De Jong suggested in 1927 (Het geheim van het Oera-Linda-Boek) that KASAMIR referred to Latin Casus Mirus (rare case).Page one of my new English Oera Linda translation (experimental phase). I have decided not to stick to the original wording, but make it a more easy read, with possibility of comparing to transliteration and original manuscript. => see separate posts here and on http://aldfryas.blogspot.de/
Posted 20 October 2015 - 07:55 AM
The Puzzler, on 20 October 2015 - 06:35 AM, said:
Interesting.Latin casus "a chance, occasion, opportunity; accident, mishap," literally "a falling," from cas-, past participle stem of cadere "to fall, sink, settle down, decline, perish"
The dutch word is "geval" (ge-val: event, case)
Posted 22 October 2015 - 04:29 PM
Thank you for the feedback, Puzzler.
The Puzzler, on 22 October 2015 - 04:11 PM, said:
We still have "Vlieland" which is pronounced "Vleeland". Verb FLY in OLB also means to flee, not to fly. See FLY.BURGH.My comment would be, the language seems a bit strange - why have Fleeland? The OLB clearly says Flyland, if the translation is English, it sounds strange.
Quote
Werser is the current eastfrisian (NW Germany) name and closer to original than Weser.Werser sounds a bit odd too, I've never heard it called that. It seems a made up name that doesn't correspond with a Frisian name.
My dictionary said "burg" is stronghold, which seemed better than Burgh and burrough to me. But I will reconsider that and the other things you wrote.
Posted 22 October 2015 - 08:49 PM
I reckoned that one of the main reasons why the OLB is not more
popular is, that the existing translations are not easy or pleasant
reads. Sandbach is a translation of Ottema's translation, it has long
oldfashioned sentences and many strange words. Interesting for experts,
but not for the more general public. The screenshots I posted earlier
still had many original names and words in italic, but in the full
translation of the first 7 pages, I had aimed at changing most of them
into easier words. It remains a dilemma sometimes, use the original
spelling, or an adaptation or even translation (of names or titles
mostly). I would for example not translate Wralda or Frya, just explain
in a footnote or introduction what the meaning is.I think I will change Werser into Weser because there is hardly any doubt that it is the same river. But Stavia or Medeasblik for example might not be at the same location as our current Stavoren and Medemblik. So I would leave them, but I turn Stavja into Stavia and Médéasblik into Medeasblik. All those accents can be discouraging and the j in English is uncommon at that place.
FLYBURGH, actually FLÍBURG/ -BURCH (and FLÍLAND):
p.63, translated as "the paths leading to our places of refuge"
p.87, untranslated: "On the other side of the Scheldt, at Flyburgt, Sijrhed presided"
p.93, idem: "went off with all his people to Flyburgt"
p.249, (USA FLÍ JEFTHA WÉRA) translated as "to the east of Liudwerd, lies our place of refuge"
The dutch word is "vlieden".
I will change "burg" into "burgh" again.
"Magus" was in my English dictionary and seemed to fit quite well. ("Magy" was not, but I could indeed leave it untranslated.)
For "FÁM" I doubted between "maiden" and "lady", but maiden i.m.o. associates with "maid" and virginity. We say "burchtvrouwe" which is more like Lady. I will reconsider.
BURGUM / BURGA are plural. Singular is only once with G only (BURGFÁMNA on p.151), usually CH or GH.
Yes indeed, sometimes authors are not consequent in spelling. I don't think BURCH and BURGH have different meaning, they are just varieties of the same word (many other examples of this phenomenon in OLB).
Thanks again for the feedback and compliment.
Posted 23 October 2015 - 09:58 AM
Thank you for the feedback, PT.Yes, I also like the idea of Fleeland being a land of refuge for the 'Free-minded'.
Quote
I had not thought of that. It is indeed a good reason not to use that spelling.Flyland in my view gives an impresion of a land infested with flies
"umbrought" - compare dutch "omgebracht", past perfect of "ombrengen", this is a eufemism for "to kill". Later in the text, page 79-85 confirms that she (last folkmother FRANA) was indeed killed.
"vrest" - dutch "overste", german "oberst": supreme or highest.
"anda" - where do you think this refers to a tribe or nation?
"go-red" - dutch "gouw-raad", german "Gau-Rat" https://en.wikipedia...ry_subdivision) ; raad/ Rat = council
"wrdon" - dutch "worden, german "werden" : to become (see context: they fell apart because they had become wet)
The comments of you both have been very helpful. I have changed into "burgh" and "maiden", "Weser" and made some more improvements. I hope all this will inspire some new discussion and insights.
Who wants to compare my draft translation so far with the one by Sandbach (1876) can look here
The Puzzler, on 22 October 2015 - 04:11 PM, said:
https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/magusWhat's wrong with 'Magy'? I don't see a need to change it to Magus. It's not a Frisian word nor an English word.
(common usage) magician, and derogatorily sorcerer, trickster, conjurer, charlatan
I thought this suited wel :-)
We have gotten used to Fám, Magy, Flyland etc., but someone reading it for the first time may get discouraged when it has many unfamiliar words. But I agree, it's a dilemma. Until recently I tried to always stay as close to the original words as possible. That I will present the new translation right next to my transliteration and the fascimile will make it very easy for the more curious readers to find the original word and spelling. Also I will add foot or endnotes.
Posted 29 October 2015 - 09:49 AM
"Tread softly" is a good translation.I have come to appreciate Sandbach more than I did. Some of his sentences cannot be improved or even equalled.
But when I can think of a solution that is different and just as good, I tend to use that and not his, to provide the reader who knows his already a fresh look.
Posted 01 November 2015 - 02:10 PM
Passing Time, on 01 November 2015 - 01:30 PM, said:
nóg - icelandiccan you be sure in this one though that Enoch , means enough , and that they are not refering to the Enoch ( cheiftains name ) from page 1 . saying that his burgh alone did not help the others ??
nog - swedish
nok - danish, norse
genug - german
genôch - frisian
genoeg - dutch
ENOCH is used several times for what must be "enough":
p.31
FÉLO SLACHTA FINDA.S SEND SNOD ENOCH. (many tribes of Finda are smart enough, but...)
MEN HJA SEND GÍRICH. HÁCH.FÁRANDE.
FALSK. VNKUS ÀND MORT.SJOCHTICH.
p.86
NÉI THAT THA FLÁTE FÉR ENOCH EWÉI WÉRE (when the fleet was far enough...)
WENDON VSA STJURAR
p.88
ELK FORST WÁNDE FORTH THAT ER ENOCH DÉDE (... that he did enough, as/when he watched over his own state)
AS ER WÁKADE OVIR SIN ÀJN STÁT
p.105
MIN HUS WÉRE STERK ENOCH SÉIDER. (my house was strong enough)
p.197
STOR ENOCH VMB HELMET ÀND SKILD TO BÉRANE (strong/ big enough to carry helmet and shield)
The chieftain's name E.NOCH thus probably means "enough".
Quote
No not the wrong order. In my final version I will probably keep the original, but I will note where the text continues chronologically. For many readers that may be easier and a more pleasant reading experience.do i take it that from your jumping about with pages , that you consider the MS to be in the wrong order ?
I think that for a new reader, it might be better to first read all about the occurrences of 6th C. BCE, before diving in the mythology, the more ancient histories and laws. That may just be to much of a mind-stretcher, and confusing.
Quote
Hidde, the last known copyist.who do you think numbered the pages ?
Quote
Yes, but not only. Literally it means the most ancient one. Sometimes it just makes more sense to translate it as World.also note that you think Wr Alda means world .
Posted 02 November 2015 - 11:59 AM
A remarkable detail.Adela advised:
"I should farther recommend that you should visit all the citadels, and write down all the laws of Frya's Tex, as well as all the histories, and all that is written on the walls, in order that it may not be destroyed with the citadels."
Then this is said:
"Adela's advice was followed.
These are the Grevetmen under whose direction this book is composed:—
Apol, Adela's husband; [...] The towns Liudgarda, [...] are under his care."
Apollania writes about her burgh in Ljudgarda:
"On the south wall the Tex is inscribed. On the right side of this are the formulae [FORM.LÉRE], and on the other side the laws"
But these were not copied into the original Book of Adela Followers, as Apollania writes:
"The old legend [FORM.LÉRE] which is written on the outside wall of the city tower is not written in "The Book of Adela's Followers." Why this has been neglected I do not know; but this book is my own, so I will put it in out of regard to my relations."
It looks like Apol, Adela's husband and responsible for having the texts of the burgh Ljudgara copied, did not think much of the FORM.LÉRA (primal teachings about Wralda), or he left it out for some other reason...
I know we can only speculate about why it was left out, but it is at least noteworthy.
Posted 12 November 2015 - 02:08 PM
The Puzzler, on 10 November 2015 - 03:10 PM, said:
No. Similar words in Dutch (and English, see words in bold):BANNALINGA seems to equate to "long banished" with banna being banished and linga=lenga=lang = long
zuigeling - infant, suckling
vluchteling - refugee, 'flightling'
dopeling - child that is being baptised, 'dipling'
sterveling - mortal, 'starveling'
tweeling - twins, 'twoling'
huurling - mercenary, hireling
zwakkeling - weakling
etc.
Posted 12 November 2015 - 08:47 PM
Van Gorp, on 12 November 2015 - 06:39 PM, said:
It is possible that JES-US was one of the various names of Buddha and that Isa (or whatever his name was) from Nazareth studied in Kashmir and took or got "Jesus" as name, after one of Buddha's names. There are also indications that he lived there after the crucifiction (that did not kill him as he was taken off the cross in time and cured from his wounds). There are good documentaries that argue for this and it is clear that this would take away one of the main foundations of the Christian doctrine.What stays remarkable if we go along with OLB is the fact that a Jesus as a Saint Isa in Kashmir is since some years in debate, only mostly not ascribed as being born there.
Posted 22 November 2015 - 05:13 PM
Ca. 3000 years old intact skeleton found in Westfriesland (near
Westwoud) - West-Flíland in the OLB - of a woman (20-25 y.o., 1.60 m
tall) in former gravemound of which only the surrounding ditch was still
visible, 30-40 cm. under surface. The chalk-rich soil had preserved the
remains so well.
Posted 24 November 2015 - 12:29 PM
Puzzler said in the old thread (29 April 2015)Back then, I didn't have the patience to find the right argument, but now while translating work, I found this:the word hell/helle for light and clarity is not Frisian. That's what no-one seems to be getting
Page 36 (Sandbach p.53):
THAT LIKT.EN ORDÉL SÉIDON THA PRESTERA.
MEN ASTE NV MÉNSTE THÀT PEST THRVCH VSA DVMHÉD KVMTH.
SKOLDE NY.HEL.LÉNJA THÀN WEL SA GOD WÉSA WILLE.
VMBE VS EWAT FON THÀT NYA LJUCHT TO LÉNANDE HWÉR VPPA HJU SA STOLTA IS.
Sandbach:
That seems very good judgment, said the priests;
but if you mean that the plague is caused by our stupidity,
then Nyhellenia will perhaps be so good
as to bestow upon us a little of that new light of which she is so proud.
My provisory translation:
"That is quite a statement," the priests said,
"but if you imply that the plague is a result of our ignorance,
then would Nyhellenia be so good
as to live up to her proud name and enlighten us?"
(wordplay will be explained in a footnote)
It is implied here that HEL can be interpreted as light.
Posted 23 December 2015 - 12:01 PM
flashman7870, on 22 December 2015 - 07:21 PM, said:
I can't recall an instance of Wr-Alda being called "God"
"GOD" in OLB is usually an adjective, meaning good or perfect.
But sometimes it is also used as a noun, to mean "god". (Also: AFGODA: idols, 'off-gods'.)
p.35
NÉAN SÉIDE MIN.ERVA.
MEN IK NE KÀN NÉNE GODA THÉR ÀRG.DVANDE SEND.
[... ] IK KÀN ÉN GODE. THÀT IS WRALDAS GÁST.
MEN THRVCH THAM ER GOD IS. DVATH.ER ÁK NEN KWÁD.
"No," Minerva said,
"since I do not know any gods that do evil,
(...) I only know one 'god', that is the world spirit (or: Wralda's spirit),
but because 'god' means good, he also does no evil."
p.99
THÉRVMBE IS WRALDA ALLÉNA GOD.
ÀND THÉR NE SEND NÉNE GODA BUTA HIM.
[...] GOD IS ALLÉNA VNFORANDERLIK.
THRVCH THAT WRALDA GOD IS
ALSA NE MÉI HI AK NAVT FOR ANDERJA.
p.103
WY FRYA.S BERN SEND FORSKINSLA
THRVCH WR.ALDA.S LÉVA. [...]
SVNDER Á SA GOD TO WRDA
AS WR.ALDA SELVA.
(...)
without ever becoming so good/ perfect (godlike)
as Wralda himself
p.158
WRALDA IS WIS ÀND GOD ÀND AL FÁRSJANDE.
NÉIDAM.ER NV WIST [...]
ALSA HETH.ER AN THJU TÁL
ÉNE RJUCHT FÉRDIGE ÀJENDOMLIKHÉD FÀST BONDEN.
[...] NÉIDAM VSA TÁLE THUS [...]
THÉRVMBE IS HJU MITH ALLE RJUCHT
GOD.IS TÁLE HÉTEN.
[...] GOD.IS.SKALKUM [...] GOD.IS ÉWA
(...)
God's language ... god's helpers ... god's laws
I left some of the fragments untranslated, so you can have some fun with them yourselves.
[In the last week of December there was suddenly much activity on the forum. I only joined in again later. A new poster that I had corresponded with already, "FromFinland" is a specialist of the "Bock Saga" and comparing various traditions. With his permission, I will copy many of his posts here.]
zxc, on 24 December 2015 - 01:58 PM, said:
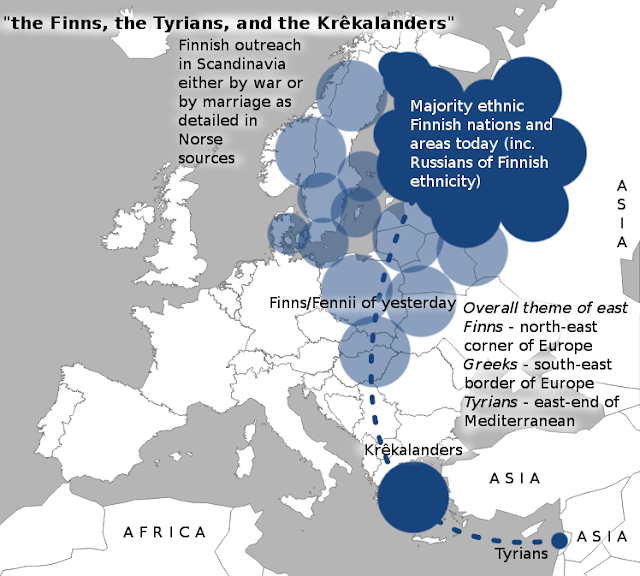
That is a good question. While study of the Over de Linden manuscript has not happened at all from the Finnish point of view, it could possibly be very valuable if it indeed spoke about Finnish peoples. There exists few known old sources speaking of Finns, to which we must also include Estonians and pre-Rurikid Russians for we are more or less the same people racially, culturally and linguistically. To an outsider, the matter of Finns in old records can be somewhat confusing:
Are Finns Finnish
- in Finnish language 'Finland' is Suomi and 'Finnish' is suomalainen
- Norse sources call Finns either by nation (Finland) or by geographical tribal distinction of Kvens, Häme people, Carelians, Ålanders, Bjarmians and so on
- some Norse sources use term Finn to refer instead to Lapps of the Lapland, who in turn are a people culturally and racially distinct from Finns and Scandinavians
- medieval Russian sources call Finns by national or tribal names like sumj (Suomi ie. Finland) or jem (Häme)
- in medieval sources 'castle of Finland' was Somelinde ie. Suomenlinna.
- Claudius Ptolemy in his Geography from around 150 AD mentions Finns (Finni) and likely also Estonians (Ossi) and Carelians (Careotae) in Baltic and Eastern European context
- Tacitus in his Germania from around 98 AD mentions both Finns (Fennii) and Estonians (Aestii)
- Finnish researcher Pasi Ockenström puts Fennii of Tacitus near Pripyat river of Belarus and notes that archeological evidence from modern-day Finland doesn't fit exactly the description of the Fennii.
I have attached a map of Northern Europe showing modern Finland, possibly Fennii of Belarus and the known locations of old Finnish military forces west of modern day Finland:
- conquering and founding Norway, as per How Norway was Settled, The Foundation of Norway, A History of Norway and indirectly confirmed by existence of very the same characters like on Iku-Turso (Fornjot) and Iku-Tiera (Thorri) son of Niera (Thorri son of Snaer) in Finnish folklore and poetry.
- Battle of Brávellir in Sweden, where according to Saxo Häme people, Ålanders and Estonians took part, all of which are Finns.
- according to the The Foundation of Norway, Goi son of Finnish king Thorri had kinsmen in Denmark.
FromFinland posted 28 December 2015 - 04:38 PM
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
Recurring themes in royal naming are common in Europe, as previously mentioned by The Puzzler. Anglo-Saxons had Aethel, Frisians apparently Adel, late Swedish kings often had Erik or Eirik as given name. Recurring naming patterns in Finnish royal or leadership context are: I) nature and winter related names, some of which are Finnish surnames still today (Halla, Pakkanen); II) Tor-related names as in king Thorri/Iki-Tiera, princess Thora, dynasty of thurses/turisas/Iku-Turso; III) age related names as in Fornjot dynasty (forn = 'ancient') of Iku-Turso and Iki-Tiera (iki = 'of age', 'ancient') and in pagan songs:Adel was the name of four Frisian kings, and we can assume it was a popular name among the Frisians, perhaps recalling a legendary sea king of old.
"Tuo oli laulaja ikuinen, = He was a singer eternal,
Virren porras polvuhinen, = step of hymn knee-high,
Tuop' on vanha Wainamoinen, = that is old Vainamoinen, [ie. Odin]
Toinen seppo Ilmarinen, = second smith Ilmarinen, [ie. Tor]
Kolmas lieto Lemminkainen, = third Lemminkainen, [ie. Balder]
Seki kaunis Kaukomieli, = he the beautiful Far-mind,
Pohjan neiti neljantena;, = young lady of North as fourth,
Pohjan neiti, Pohjan akka, = young lady of North, old woman of North,
Viies Antero Wipunen, = Antero Vipunen the fifth,
Se kuues Kaleva vanha. = that sixth Kaleva the Old. [father of Vainamoinen and Ilmarinen]
Viel' oli nuori Joukahainen, = Still there existed young Joukahainen,
Viela muitaki monia, = and many others,
Joit' ennen isoni lauloi, = of which my father used to sing of,
Oma vanhempi opetti." = my own elder taught of. (Kanteletar, song 278.)
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
Variation of this theme was included in a 1996 book written by Finnish tour guide and former actor Ior Bock (1942-2010), according to whom he was taught orally an old family saga between 1949-1969 by his adoptive family of Rachel Boxstrom (1888-1976) and Rhea Boxstrom (1899-1984). Namely, ice age was known in this bi-lingual family tradition as allt land is, meaning 'all land ice'. It ended in a catastrophical way 8016 BC when the warm water from Atlantic melted the huge ice blocks, resulting in an ice slide destroying most of the Nordic lands in process, save for few forefathers of the Nordic white race who survived and later on spread outwards from the island of Gotland. Unfortunately, this family saga has received very little academic interest and as of 2015 there doesn't exist any deep studies of it.In early times almost all the Finns lived together in their native land, which was called Aldland, and is now submerged.
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
What is the East Sea on this context? Baltic Sea is called 'East Sea' in some European languages.Eastward our boundary went to the extremity of the East Sea
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
If anyone desires to research the British aspect of this story, I recommend to have a look at Geoffrey of Monmouth's The History of the Kings of Britain and the traditions behind it. They have it the other way around: Britain of Britons was a high society of learning and culture, that was ravaged by barbaric Angles and Saxons. This is a pattern where one's own culture is usually shown to be the only true, right and proper way of life, typically under existential foreign threat.Opposite to us we had Britain, formerly Westland, with her tin mines. Britain was the land of the exiles, who with the help of their Burgtmaagd had gone away to save their lives; but in order that they might not come back they were tattooed with a B on the forehead, the banished with a red dye, the other criminals with blue. ... Saxmannen, because they were always armed against the wild beasts and the savage Britons.
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
In chapter XIII of The Norsemen the British historian Helene Adeline Guerber notes the following: "In the course of a walk along the sea-shore Odin once beheld nine beautiful giantessess, the wave maidens, Gialp, Greip, Egia, Augeia, Ulfrun, Aurgiafa, Sindur, Atla, and Iarnsaxa, sound asleep on the white sand." In addition, in Finnish language 'wave' is aalto.Aldland, called by the seafaring people, Atland, disappeared, and the wild waves rose so high over hill and dale that everything was buried in the sea.
New and returning posters welcome!
I thought the thread was dying, but it looks like we can breath some new life in it.
I don't have the inspirtation yet to reply to posts, although some of it is very interesting, but today on a trip I made some pictures that I think are fascinating.
It was in a small German village (Rimbach, Bornhagen) and shows how the 6 spoke wheel was integrated into the Christian symbology:
 Both were taken at the same old tavern and I also saw meat hanging from a
tree there, which I heard is an ancient (prechristian) tradition around
yule/ midwinter (it shows that religious christian people still have
kept some of the much older ways):
Both were taken at the same old tavern and I also saw meat hanging from a
tree there, which I heard is an ancient (prechristian) tradition around
yule/ midwinter (it shows that religious christian people still have
kept some of the much older ways):
Posted 28 December 2015 - 07:24 PM
Abramelin, on 28 December 2015 - 05:56 PM, said:
Your logic is flawed.Hence it must be younger than the original etymology, and hence younger than, say, the 12th century
OLB has THJUD for people/ folk.
TWISK is another word, meaning between, like english (be)twixt, saterland frisian twiske.
Some examples:
TWISK ANNEN GRÉVET.MAN AND THA MÉNTE
TWISK THÀT BERCHTA EN BURCH BVWA
VPPA GRVND TWISK THA SÛDLIKA HÛSA
Nowhere it is suggested that TWISKLAND is THJUD.S.LAND.
Thy could roughly refer to the same area, and they could be related by association, but it proves nothing.
FromFinland posted 28 December 2015 - 08:52 PM
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
This reminds me of two parallels:One hundred and one years after the submersion of Aldland a people came out of the East. That people was driven by another.
- Authors of Wikipedia state: "Cited by the 4th-century historian Ammianus Marcellinus, Timagenes
(1st century BC) describes how the ancestors of the Gauls were driven
from their native lands in eastern Europe by a succession of wars and
floods."
- Fridtjof Nansen's study on fate of the Finnish Bjarmians in Medieval times, page 140: "The name of the Bjarmas themselves disappears after the middle of the thirteenth century, when it its related that a number of Bjarmas fled before the "Mongols" and received permission from King Håkon to live in Malangen fjord." (There is also stuff on Frisians starting right from page 147.)
FromFinland posted 29 December 2015 - 12:08 AM
Hélène Adeline Guerber of Britain has the following story to share on the origins of the Frisian laws, as seen in chapter XII of her book Myths of the Norsemen:
"The Story of Heligoland
In
order to facilitate the administration of justice throughout their land
it is related that the Frisians commissioned twelve of their wisest
men, the Asegeir, or elders, to collect the laws of the various families
and tribes composing their nation, and to compile from them a code
which should be the basis of uniform laws. The elders, having
painstakingly finished their task of collecting this miscellaneous
information, embarked upon a small vessel, to seek some secluded spot
where they might conduct their deliberations in peace. But no sooner had
they pushed away from shore than a tempest arose, which drove their
vessel far out to sea, first on this course and then on that, until they
entirely lost their bearings. In their distress the twelve jurists
called upon Forseti, begging him to help them to reach land once again,
and the prayer was scarcely ended when they perceived, to their utter
surprise, that the vessel contained a thirteenth passenger.
Seizing
the rudder, the newcomer silently brought the vessel round, steering it
towards the place where the waves dashed highest, and in an incredibly
short space of time they came to an island, where the steersman motioned
them to disembark. In awestruck silence the twelve men obeyed; and
their surprise was further excited when they saw the stranger fling his
battle-axe, and a limpid spring gush forth from the spot on the
greensward where it fell. Imitating the stranger, all drank of this
water without a word; then they sat down in a circle, marvelling because
the newcomer resembled each one of them in some particular, but yet was
very different from any one of them in general aspect and mien.
Suddenly
the silence was broken, and the stranger began to speak in low tones,
which grew firmer and louder as he proceeded to expound a code of laws
which combined all the good points of the various existing regulations
which the Asegeir had collected. His speech being finished, the speaker
vanished as suddenly and mysteriously as he had appeared, and the twelve
jurists, recovering power of speech, simultaneously exclaimed that
Forseti himself had been among them, and had delivered the code of laws
by which the Frisians should henceforth be judged. In commemoration of
the god’s appearance they declared the island upon which they stood to
be holy, and they pronounced a solemn curse upon any who might dare to
desecrate its sanctity by quarrel or bloodshed. Accordingly this island,
known as Forseti’s land or Heligoland (holy land), was greatly
respected by all the Northern nations, and even the boldest vikings
refrained from raiding its shores, lest they should suffer shipwreck or
meet a shameful death in punishment for their crime.
Solemn
judicial assemblies were frequently held upon this sacred isle, the
jurists always drawing water and drinking it in silence, in memory of
Forseti’s visit. The waters of his spring were, moreover, considered to
be so holy that all who drank of them were held to be sacred, and even
the cattle who had tasted of them might not be slain. As Forseti was
said to hold his assizes in spring, summer, and autumn, but never in
winter, it became customary, in all the Northern countries, to dispense
justice in those seasons, the people declaring that it was only when the
light shone clearly in the heavens that right could become apparent to
all, and that it would be utterly impossible to render an equitable
verdict during the dark winter season. Forseti is seldom mentioned
except in connection with Balder. He apparently had no share in the
closing battle in which all the other gods played such prominent parts."
The story is interesting for many reasons. Let's examine it more closely:
”twelve of their wisest men, the Asegeir, or elders”
Ior Bock of Finnish Boxström saga had this to say on the topic, from his 1996 book page 19 with my translation:
”Lag … Twelve people sat together and formed the law. Law has a logic that it follows. Law is in the vaner language [Finnish language] laki and logic and means also a team such as footboll team. In team the law is created.” And it just so happens, that in the Boxström saga it is the asers of South Finland creating the laws and maintaining the social norms.
”to collect the laws of the various families and tribes composing their nation”
As Frisians consist of many tribes, it confirms this manuscript quote by Tony S.:
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
As our country was so great and extensive, we had many different names.
”then they sat down in a circle”
As above, but may also refer to the allting, which the Finns also had.
”who might dare to desecrate its sanctity by quarrel or bloodshed”
Sounds like holmgang is forbidden over there. The practise was not limited to Norsemen, for Britons practised it, and so did Finns too.
”Accordingly this island, known as Forseti's land or Heligoland (holy land), was greatly respected by all the Northern nations, and even the boldest vikings refrained from raiding its shores”
Likewise, in Finnish context Helsinki was founded upon Helsingeå and in Boxström saga Hel of South Finland was indeed a 'holy land' (hel = heliga, 'holy') where only the Finns of aser cultural background lived.
”people declaring that it was only when the light shone clearly in the heavens that right could become apparent to all”
Again, in Finnish context of the Boxström saga it is highlighted how whole of the culture radiates from the sun first to the ruling family of deciders and finally to the common people. With the royal family members having symbolical roles of sun and moon, the latter shining down the light from the first.
Overall, the idea of sacred island reminds of the Anglesey of the druids, who were also judges. In Finnish Boxström saga, this same function is held by island of Susisaari outside Helsinki. In this respect, story of Frisian holy land of Heligoland sounds not only feasible but also fits a larger European cultural pattern very well.
FromFinland posted 29 December 2015 - 05:23 PM
Hélène Adeline Guerber said:
Just found out, this is a direct cultural reference to the Gladsheimr of the Æsir as described by authors of Wikipedia:... Frisians commissioned twelve of their wisest men, the Asegeir, or elders ...
"Snorri states in Gylfaginning that Glaðsheimr is a meeting hall containing thirteen high seats where the male Æsir hold council, located in Iðavöllr in Asgard, near the hall of Vingólf where the Ásynjur goddesses gathered."
Thirteen seats - as opposed to twelve seats - may be a reference to the twelve Asegeir plus Forseti the chief law giver. Same number applies also in Finnish sources, whether it's the Boxström's aser ruler and his twelve sons, or general Kaleva and his twelve sons, as known from Kristfrid Ganander's records and the Anglo-Saxon Widsith (line 20).
FromFinland posted 29 December 2015 - 06:07 PM
Passing Time, on 29 December 2015 - 10:15 AM, said:
To my mind it seems that there have been many - not just one - cataclysms in Europe of the past. Most people know of the Minoan eruption and fate of Pompeii. The Estonian craters seem to belong to this category also, as do the Tunguska and more recent Chelyabinsk events. As many others have noted here, people sometimes use same words for both natural and man-made causes. For example, it's not uncommon to read headlines about 'flooding' immigrants, 'storming' immigrants or Europe being 'on fire'. In Boxström saga the term Ragnarök is applied to three separate causes: cosmological, geological end of last ice-age and finally a man-made genocide. Just as much of the ancient iconography and legends seems to stem from biochemical sources, so does there seem to be a constant cosmological sway.it could have been this impact that caused the upheaval of the land which killed the mother after her speech
FromFinland posted 30 December 2015 - 02:59 PM
zxc, on 24 December 2015 - 02:56 PM, said:
From Finnish and Nordic point of view it is the contact between the Finns and Frisians that raises eyebrows in Oera Linda book, as everybody knows that there have been for many centuries Germanic and Scandinavian nations in between, and are still of today. My point was to highlight the later Iron Age Finnish outreach in the Western Scandinavia, from which it isn't anymore that far to the Frisian areas. If such things were reality in Iron Age, surely the more earlier accounts told of in the Oera Linda book could be precursors to that. (That is, they would make a recurring pattern.)I know people move about and that the old Finns may have been elsewhere to the modern Finns, nevertheless, the map on the site I linked to above seems to show that at the height of their (empire)? the borders stopped at Denmark and this is of course short of Finland.
Of course, we the selected few (
And I shall again quote mr. Bock from 1996 (page 67), my translation:This certainly opens the possibility that the name Over de Linden refers not to a tree, but to a 'castle'. (...)
"Castles and lines [linnat ja linjat]
The crown of Seppo
Ilmarinen is a crown of a fir tree, a 'fir's crown' that is. The leaf of
a palm tree and twig of a fir are similar in shape. In both grow
spikes, which symbolise "lines". In tropical times symbol of a king was a
palm tree leaf, and a fir twig in the arctic period. [...] Castle comes
from the word line. There were lines of different types [...] For this
Seppo's offering system there were hill forts [linnavuoria],
on top of which buildings were often erected. Seppo had a possibility
to leave [Aesir province of] Uudenmaa by going from castle to castle. As
not all people were allowed to come to Uudenmaa, for that reason for
example Kyrö castle [Olavinlinna]
was situated outside the Uudenmaa [...] Also Maija Ilmatar [queen's
title] could leave Uudenmaa by going from castle to castle. A line leads
to a castle"
Same book also goes on to highlight the meaning of the family trees (page 38) and includes a variant on the Norse story of Ask and Embla.From Väinämöinen's (i.e. Odin's) moral code on a good living we can find the following detail:
"Sitä kuusta kuuleminen, = Listen to that fir tree
Jonka juuressa asunto." = at the base of which lies the house. (Kanteletar, first book, song 90.)
Likely
this refers to Finnish folk practice of planting a tree at the exact
spot, where one saw an elf-spirit while dreaming as a part of a ritual
to check if a plot of land was suitable for building work. This clearly
pre-Christian ritual is known to be practiced in the later Christian
times, as it is represented in Elina and Maija Ranta's book Haltijoitten mailla, maahisten majoilla (WSOY 1996).
Posted 30 December 2015 - 06:12 PM
Abramelin, on 30 December 2015 - 05:17 PM, said:
This is the right etymology for Twiskland: Þeodscland/Þeodiscland/Theodiscland >> Twiskland
twisk - twisch - zwisch(en) - tussch(en)
thiudisk - duutsc, dútsk - duitsch, tsjutsk
BTW so called 'folk etymology' may very well be just as old as what you call 'original' etymology.
In other words, our ancient ancestors may already have played with ambiguity and associative naming.
I think the alleged god Tuisco was made up to provide for the people who identified with living in 'Tuiscland'.
The Scandinavian version Tyskland may have come from 'twisk', while Deutsch and Dutch will come from thjud.
FromFinland posted 01 January 2016 - 03:05 PM
Ell, on 31 December 2015 - 11:47 PM, said:
Might this also be translated as "at the top of which lies the house"?
"If
you got a permission from the land owner for building work, do not
raise your house at the exact point where the elf-spirit stood in your
dream, but plant there a tree instead. If it happens that you'll die
before making a testament, your heirs will find with the help of the
tree what was your wish. They must cast a ballot to have one person, who goes to sleep under the tree. The elf-spirit of the plot of land will come to the sleeping persons dream and tells, how you would have wanted the heirs to act on the inheritance."
The Boxström saga details the heathen belief in elf-spirits and they are detailed as beneficial, as in house-keepers taking care of the household animals and so on (Bock 1996, p. 57). In this regard it parallels the Finnish folk customs still practised in the 19th century countryside.
From the Oera Linda book I read:
"23. THIS IS INSCRIBED ON THE WARABURGT BY THE ALDEGAMUDE. [...]
This
people have not even a name; but we call them Finns, because although
all the festivals are melancholy and bloody, they are so formal that we
are inferior to them in that respect. But still they are not to be
envied, because they are slaves to their priests, and still more to
their creeds. They believe that evil spirits abound everywhere, and enter into men and beasts, but of Wr-alda’s spirit they know nothing. [...]
43. THIS WRITING HAS BEEN GIVEN TO ME ABOUT NORTHLAND AND SCHOONLAND[...]
Moreover, they believe in bad spirits, witches, sorcerers, dwarfs, and elves, as if they descended from the Finns."
We Finns surely were known as sorcerers by other Europeans and for selling wind for mariners still in the historical times: "In the north live lots of wizards, sorcerers and witches. Finnish wizards are able to sell wind" (Olaus Magnus 1555). Finns were likewise seen as sorcerers by pagan Scandinavians, as seen here ("might and magic followed Norr and his men"), here (chapters 16. and 17.) and here.
Posted 01 January 2016 - 06:32 PM
TIN.LÁNA (and spelling varieties) was translated by Ottema
(1872/1876) as "tinlanden" (tinlands) and SULVER.LÔNA as "zilverlanden"
(silver lands). Jensma (2006) left this unchanged.Sandbach (1876) translated TIN.LÁNA as "tin mines" and SILVER.LÔNA as "silver countries".
Nowhere else in the OLB is land or lands spelled without a "d".
Once LÔNE is used separately, which was not translated by Sandbach, while Ottema had "laan" (lane).
I suspect that this is actually the same word as in the 'mining' context. On wiki I read that ancient tin mining in Cornwall was not done deeply in the earth, but in superficial streams (straight lines). So I suppose that "tin lanes" and "silver lanes" would be a good alternative to the existing translations. See fragments and original translations below.
LÔNE - 8 (fragment number)
TIN.LÁNUM - 1,4
TIN.LÁNA - 2,3,5,6
(ÍSER JEFTHA TIN LÁNA - 2)
TINLÔNUM - 9a
TINLÔNA - 9b
SULVER.LÔNA - 7
OLB fragments [page/ line]; O-S = Ottema Sandbach page nr.
1 [042/05] O-S p.61
STÉLTH I JETA RÉIS THÀN MOT HI NÉI THA TIN.LÁNUM
For a second offence he shall be sent to the tin mines
Steelt hij dan nog eens weer, dan moet hij naar de tinlanden
2 [042/19] O-S p.61
JEF I INNA ÍSER JEFTHA TIN LÁNA MÉI WERKA
... to work in the iron or tin mines
of hij in de ijzer- of tinlanden mag werken
3 [042/24] O-S p.61
KÀN SINE BURCHFÁM HIN FAR ALTID NEI THA TIN.LÁNA HELPA
if the Burgtmaagd can (forever) send him to the tin mines
kan zijne burgtmaagd hem voor altijd naar de tinlanden helpen
4 [042/30] O-S p.63
SA MOT I THACH NÉI THA TIN.LÁNUM
he must go to the tin mines (after all)
dan moet hij toch naar de tinlanden
5 [043/21] O-S p.63
MEN NAVT NÉI THA TIN.LÁNA
but not to the tin mines
maar niet naar de tinlanden
6 [048/08] O-S p.69
BRITTANJA MITH SINA TIN.LÁNA. [...] WAS THAT LAND THÉRA BANNALINGA
Britain (...) with her tin mines (...) was the land of the exiles
Brittannie met zijne tinlanden (...) was het land der ballingen
7 [078/12] O-S p.109
ET SULVER THÀT THA SLÁVONA UTA SULVER.LÔNA WNNON
the silver that their slaves got in the silver countries
het zilver, dat de slaven uit de zilverlanden wonnen
8 [095/14] O-S p.133
FOLLISTAR KÉMON OMME HERNE THÉRE LÔNE WÉI
Reinforcements came (from around the corner of the lane)
Helpers kwamen om den hoek van de laan weg
9 [198/24] O-S p.239
BRITNE ÀND BANNENE THÉR BÍ GRÁDUM MITH TÍD
FON ÛT.A TINLÔNUM THÉR HINNA FLJUCHTE.
THÉR UT.A TINLÔNA KÉMON HÀVATH ALGADUR
VRLANDISKA WIVA JEFTHA FON VRLANDHIS TUK.
Britons and fugitives who gradually, in the course of time,
took refuge there from the tin mines.
Those who come from the tin mines have wives,
either altogether foreign or of foreign descent.
Britten en vluchtelingen, die allengs met der tijd
uit de tinlanden derwaarts vluchtten.
Die uit de tinlanden kwamen, hebben al te gader
buitenlandsche vrouwen of van buitenlandsch ras.
Note that even in two consecutive sentences there can be spelling variety (fragment nine), or on one page (fragments 1-4).
Posted 02 January 2016 - 04:36 PM
The Puzzler, on 02 January 2016 - 01:58 PM, said:
Yes, in current Frisian dialects, the "d" may be left out, but consider this:LON and LAN is land in Northfries and variants in bolded bit below.
Tinlána (and varieties) is nowhere spelled with a "d" and nowhere (else) in the OLB is "land" spelled without the "d":
LAND 96X
LÁND 57X
LANDA 47X
LÁNDA 8X
LANDAR 19X
LÁNDAR 6X
LANDUM 13X
LÁNDUM 5X
LÁNDER 2X
TEXLÁND 2X
SKÉNLAND 6X
SKÉNLÁND 2X
ÁTLAND 5X
VRLANDISKA 5X
TEXLAND 4X
KRÉKALANDAR 4X
LANDE 3X
TWISKLANDAR 3X
KRÉKALANDA 3X
ÉLAND 3X
KRÉKALANDER 2X
FLÍLAND 2X
SKÉNLANDER 2X
ALDLAND 2X
ÁLDLAND 2X
the following all 1X:
VPSALÁNDUM
LÁNDON (verb)
TWISKLÁNDAR
VRLÁNDISKE
FLÍLÁND
FLÍLÁNDA
LÁNDICH
INLÁNDISKA
TWISKLÁND
KRÉKALÁNDA
ÁTLÁND
LÁNDESKA
ÉGIPTALÁNDA
ÉLÁND
BROKLÁND
FLÍLÁNDIS
LÁNDSATON
KRÉKELANDA
VRLANDASKA
LANDWÉR
VRLANDISK
SÛDARLANDA
VRLANDHIS
TWISKLANDA
LANDIS.TAL
LANDWÉRAR
SKÉNLANDIS
LANDSÁTA
WRLANDISK
KRÉKALANDUM
ÉLANDA
BROKLAND
LANDESKE
LANDESKA
ÁLANDUM
ÁLANDAR
SÉLANDAR
(in one text only:)
LÔND 5X
LÔNDUM 1X
(note: sometimes it's hard to distinguish Á or À from simply A)
The Puzzler, on 02 January 2016 - 01:58 PM, said:
I think -mines is better than -lands and thought this was an example of Sandbach's translation being better than the ones by Ottema and Jensma, but then why did he translate "silver countries" and not "silver mines"?It might be why Sandbach has MINES for lana.
Apol posted 02 January 2016 - 06:42 PM
Regarding: LÔNA, LÂNA:Jan de Vries (Nederlands etymologisch woordenboek) and Douglas Harper (www.etymonline.com) explain Old Norse lön (plural: lanar) as ‘row of houses’, ‘way/road’, ‘barn’. Marius Hægstad and Alf Torp (Gamalnorsk ordbok med nynorsk tyding), however, translate it as ‘elongated pile or heap’. It is undoubtedly the same word in question, and ‘elongated pile or heap’ explains exactly what it is about.
From Finland posted 02 January 2016 - 08:24 PM
Apol, on 02 January 2016 - 05:16 AM, said:
If we do some little discourse analysis, it's easy to note how Finns are listed as among the other eastern nations, which is in the geographical sense true (see the attached map).In her time, Finda had also invented a script; but it was so high-flown and full of frizzles and curls that the descendants soon had lost the meaning of it. Afterwards they had learnt our script, by name the Finns, the Tyrians, and the Krêkalanders.
There is some disagreement whether the Central European Fennii are the same as the Nordic Finns (like me). Pasi Ockenström lists in his book (Fenni vai ei 2010, title means 'Fenni or not' in English) some clues:
Central European Fennii:
- described very primaevel for their time, as confirmed by archeological research of G. V. Styhov with iron tools replacing stone and bone items not until the first centuries AD (!)
- described as wild and brutal ('feritas' by Tacitus), matching the later mention in Nestor's chronicle of backwardish and wild Severian people moving from the area of modern Poland to Russian areas
- Tacitus's description puts them in the approximate area of Belarus, where the topology matches regarding the mountains
- Fennii may come from fen, a bog or a swamp.
Nordic Finns:
- same technology level as neighbours, including metal tools and weapons
- always described as peaceful and military activity depicted usually either as of defensive or reactive in type (even the Norway episode presented as a rescue operation)
- lived always here as long as everybody knows and sources always put at the Nordic area
- likewise name Suomi may come from suo or 'swamp', suomaa 'swamp-land' amongst many other speculations.
Mr. Ockenström's conclusion is that the Central European Fennii may be a separate people from the Nordic Finns. They are known to have disappeared from the history scene by the Russia's Rurikid period when their remnants moved to the Russian areas together with many other Slavic tribes. That is, they as western migrants mixed up with the native ethnic Finns of Nordic type and the few Scandinavian immigrants of viking heritage. That Finn/Fennii is not a direct reference to person's ethnicity and cultural background is confirmed also by the fact that Lapps have sometimes been referred to as 'Finns' by Scandinavians, whereas the Northern Finns living next to them were called Kvens (from Kainuu and Kajaani) or Carelians, with the people of Southern Finland being called Finns of Finland by same sources. Yet the Kvens and Carelians are just as 100 % pure ethnic and cultural Finns, unlike the Lapps of Lappland.
We may of course ponder if those Fennii of Tacitus were only a pitiful remnant of once greater Fennii-tribe, and whether they and us the Nordic Finns were merely different tribes of the same people to begin with:
Oera Linda book said:
I'm personally not so sure as to what to make of this all, as names like Finn are also known amongst the Scandinavians (popular viking name Thorfinn), Irishmen (popular recurring king's name) and Frisians (again a king's name). If you ask my opinion for the least likely scenario, it is the theory of Asian origins which is belied by studies on the distribution of blond hair and blue eyes.They divided themselves into two crowds. Each host went its way. From the first part no word has come to us, but the other part fell afterwards into our Skênland.
Apol, on 02 January 2016 - 07:13 PM, said:
(...)
Finda may possibly be identical with an old Wendic (“Findic”) mother goddess of pre-Celtic origin, named Vinda (Vindo, Uinda, Uindo, Uinde). (...) Vinda is closely related to the old mother and reindeer goddess Bovinda, who has roots back in the Neolithic age. It probably is about the same deity.
Bovinda did in turn probably originate in India, where we find Govinda as one of the many names for the Hindu god Krishna. The word is composed of go (‘cow’) and wind (‘find’), meaning ‘cow finder’, i.e. ‘cow shepherd’, and which seems to confirm that Finda means ‘to find’ – but in the significance of ‘to find for protection’.
Finda may possibly be identical with an old Wendic (“Findic”) mother goddess of pre-Celtic origin, named Vinda (Vindo, Uinda, Uindo, Uinde). (...) Vinda is closely related to the old mother and reindeer goddess Bovinda, who has roots back in the Neolithic age. It probably is about the same deity.
Bovinda did in turn probably originate in India, where we find Govinda as one of the many names for the Hindu god Krishna. The word is composed of go (‘cow’) and wind (‘find’), meaning ‘cow finder’, i.e. ‘cow shepherd’, and which seems to confirm that Finda means ‘to find’ – but in the significance of ‘to find for protection’.
Posted 03 January 2016 - 11:42 AM
FromFinland, on 02 January 2016 - 08:24 PM, said:
Again, an excellent post. So much good stuff.I'm personally not so sure as to what to make of this all, as names like Finn are also known amongst the Scandinavians (popular viking name Thorfinn), Irishmen (popular recurring king's name) and Frisians (again a king's name). If you ask my opinion for the least likely scenario, it is the theory of Asian origins which is belied by studies on the distribution of blond hair and blue eyes.
I think there has indeed been confusion about tribal names, which is also illustrated by the many names for Germany, see map:
Another thing to consider is that already in the earliest times, the Magí consciously mixed his blood with that of the Fryas:
pp.55-56 (Sandbach p.79)
pp.55-56 (Sandbach p.79)
Quote
The negative feelings of the Fryas for the "Finns" may have been based mostly on the Magí and his army (of "Finns") conquering ever more parts of "Fryasland" (specially in the 6th c. BCE when the "Book of Adela Followers" would first have been compiled), but most people simply living in the lands that were ruled by the Magí (among which what is now "Finland") may still just have been of original indigenous (blond and blue eyed) stock.When Wodin returned, Magy gave him his daughter to wife. (...) His reign lasted seven years, and then he disappeared. The Magy said that he was taken up by their gods and still reigned over us, but our people laughed at what they said. (...) but the Magy did just as he pleased, because his daughter had a son by Wodin, and he would have it that this son was of high descent. While all were disputing and quarrelling, he crowned the boy as king, and set up himself as guardian and counsellor.
Posted 03 January 2016 - 03:52 PM
Apol, on 03 January 2016 - 03:09 PM, said:
Yes, I agree. Very well said.(...)
The part of Finda’s people against whom the Freyjans had such a grudge, seems to have been largely the same peoples who in our time have adopted Islam. It may thus appear that the European fear of Islam runs deep in history – long before the raise of Islamism. On page 71/26-29 Greece is conferred to Finda’s people, while the country today must be regarded as conquered by Freyja’s culture. The border has been moved to neighboring Turkey.»
I think that Finda's people originally was the straight-black-haired Asians, but that it all became mixed up after the natural catastrophe of 2193 BC. (...)
FromFinland posted 03 January 2016 - 04:38 PM
I'll continue again
in my research by comparison, first between Oera Linda book and the
Boxström saga, then the secord part between Oera Linda book and the
Norse sagas as another post.I) This is a little comparative analysis between Oera Linda book and Boxström saga (1996 book with my translations). First we have a piece of text from the Oera Linda book:
Now We Will Write about the War between the Burgtmaagden Kalta and Min-erva,
And how we thereby lost all our southern lands and Britain to the Golen.
Near the southern mouth
of the Rhine and the Scheldt there are seven islands, named after
Frya’s seven virgins of the week. In the middle of one island is the
city of Walhallagara (Middelburg), and on the walls of this city the
following history is inscribed. Above it are the words “Read, learn, and
watch."
Let's tear it apart to see if it has any similarities to the Boxström saga:
"Near the southern mouth of the Rhine and the Scheldt there are seven islands, named after Frya's seven virgins of the week."
Pages 12 and 47:
Viapori [naval fortress
of Suomenlinna] was in our stories the Paradise Islands or the Sun
Islands. […] After the ice age here was Hel, a city of Hel. All of this
was destroyed the year 1050 [...]
At the great church of
Stockholm a paper was signed 16.7.1750, according to which Helsinki's
seven islands were to be made into Sveaborg [Swedish name for the
fortress of Suomenlinna]. That is, 700 years later, at 16.7 our old holy
islands were made to be a Sveaborg. That's why my mother [Rhea Boxström
1899-1984] got interested to find out what had happened at Viapori
[Suomenlinna], because for her it had been known as Odensö [Oden's
island] and Odensborg [Oden's castle] […] The central island of the
Hel's seven islands was Oden's island
I note that in the Boxström saga the islands are not named after the days of the week, but by other mythological names.
"In the middle of one island is the city of Walhallagara (Middelburg)"
Pages 40, 51 and 79:
At the middle of
Uudenmaa was a mountain called Listening Mountain, or Lyssnarberget. At
the middle of the Listening Mountain was a hole, the midpoint of the
planet […] It was Valhalla […] Hel was the centre point of the
Uudenmaa's aesir, that's why it was called Aas-Hel. Hel was […] a city.
It was the Midgården of the stories at the place of current Helsinki.
There existed a saying ”Hel stan var den heliga staden och vetenskap
från Hel var helvetet”, that is: Hel was a holy city and information
coming from Hel was ”helveten” [hell], or knowledge from Hel. […] val
means elections [as in 'validate'], hall a hall and a the aesir.
"and on the walls of this city the following history is inscribed"
Page 47 on Midgård:
A ring-shaped wall surrounded the towers
"Above it are the words “Read, learn, and watch.”"
Page 5:
My mother and my sister [Rhea and Rachel Boxström] have given this mythology to me. They told stories and held discussions. Both of them were in attendance, otherwise one coudn't speak of the matter. If one made small mistake, another would correct it. […] When they told stories, I was not allowed to say a word. Mother always said that one learns better by listening than by speaking. Storytelling took place so that one sat at the floor near the fireplace and at the light of the candles.
Surely I am not the only one who sees the thematic connection here?
Second part of the research by comparison, this time between Oera Linda book and the Norse sagas.
II) We start again with a piece of text from the Oera Linda book, I have bolded the parts of interest:
This is a variation of a Nordic legend, as seen in Hélène Guerber's Myths of the Norsemen, chapters XIV and XVI:
”Odin bade Hermod don his armour and saddle Sleipnir, which he alone, besides Odin, was allowed to ride, and hasten off to the land of the Finns.
[…]
The most noted of these Finnish magicians was Rossthiof (the horse thief) who was wont to entice travellers into his realm by magic arts, that he might rob and slay them; and he had power to predict the future, although he was always very reluctant to do so.
[…]
Rossthiof now began to explain the omens which his art had conjured up, and he declared that the stream of blood portended the murder of one of Odin’s sons, but that if the father of the gods should woo and win Rinda, in the land of the Ruthenes (Russia), she would bear him a son who would attain his full growth in a few hours and would avenge his brother’s death.
[…]
Billing, king of the Ruthenes, was sorely dismayed when he heard that a great force was about to invade his kingdom, for he was too old to fight as of yore, and his only child, a daughter named Rinda, although she was of marriageable age, obstinately refused to choose a husband from among her many suitors, and thus give her father the help which he so sadly needed.
[…]
His services being joyfully accepted, it was not long ere Odin—for it was he—won a signal victory, and, returning in triumph, he asked permission to woo the king’s daughter Rinda for his wife.
[…]
The prophecy of Rossthiof was now fulfilled, for Rinda duly bore a son named Vali”
It must be noted here that if this story has any connection whatsoever to the real past, the Russia of Billing and Rinda here must surely be of pre-Rurikid Finnish age. For example, name of the princess ”Rinda” means 'breast' or 'chest' in Finnish (rinta). Such call-names are well known from Finnish heathen poetry, where a lady might be called for example 'tinchest' or 'tinbreast' (tinarinta) after her rich jewerly.
As the Magy of the Oera Linda book has a strong thematic connection of the east, you'll surely see the parallel to Russia in Norse story above. Overall this reminds of the story of Balder, of which we know both legends of mythical type and the legends of more historical type.
II) We start again with a piece of text from the Oera Linda book, I have bolded the parts of interest:
When Wodin returned, Magy gave him his daughter to wife.
Whereupon he was incensed with herbs; but they were magic herbs, and by
degrees he became so audacious that he dared to disavow and ridicule
the spirits of Frya and Wr-alda, while he bent his free head before the
false and deceitful images. His reign lasted seven years, and then he
disappeared. The Magy said that he was taken up by their gods and still
reigned over us, but our people laughed at what they said. When Wodin
had disappeared some time, disputes arose. We wished to choose another
king, but the Magy would not permit it. He asserted that it was his
right given him by his idols. But besides this dispute there was one
between the Magyars and Finns, who would honour neither Frya nor Wodin;
but the Magy did just as he pleased, because his daughter had a son by Wodin, and he would have it that this son was of high descent.
This is a variation of a Nordic legend, as seen in Hélène Guerber's Myths of the Norsemen, chapters XIV and XVI:
”Odin bade Hermod don his armour and saddle Sleipnir, which he alone, besides Odin, was allowed to ride, and hasten off to the land of the Finns.
[…]
The most noted of these Finnish magicians was Rossthiof (the horse thief) who was wont to entice travellers into his realm by magic arts, that he might rob and slay them; and he had power to predict the future, although he was always very reluctant to do so.
[…]
Rossthiof now began to explain the omens which his art had conjured up, and he declared that the stream of blood portended the murder of one of Odin’s sons, but that if the father of the gods should woo and win Rinda, in the land of the Ruthenes (Russia), she would bear him a son who would attain his full growth in a few hours and would avenge his brother’s death.
[…]
Billing, king of the Ruthenes, was sorely dismayed when he heard that a great force was about to invade his kingdom, for he was too old to fight as of yore, and his only child, a daughter named Rinda, although she was of marriageable age, obstinately refused to choose a husband from among her many suitors, and thus give her father the help which he so sadly needed.
[…]
His services being joyfully accepted, it was not long ere Odin—for it was he—won a signal victory, and, returning in triumph, he asked permission to woo the king’s daughter Rinda for his wife.
[…]
The prophecy of Rossthiof was now fulfilled, for Rinda duly bore a son named Vali”
It must be noted here that if this story has any connection whatsoever to the real past, the Russia of Billing and Rinda here must surely be of pre-Rurikid Finnish age. For example, name of the princess ”Rinda” means 'breast' or 'chest' in Finnish (rinta). Such call-names are well known from Finnish heathen poetry, where a lady might be called for example 'tinchest' or 'tinbreast' (tinarinta) after her rich jewerly.
As the Magy of the Oera Linda book has a strong thematic connection of the east, you'll surely see the parallel to Russia in Norse story above. Overall this reminds of the story of Balder, of which we know both legends of mythical type and the legends of more historical type.
I just realised that this very the same myth is buried deep also in the
Boxström saga, though it's a little more difficult to notice it at first
glance. Please follow me: here it's the Finland Swedish speaking Aesir of Uudenmaa (i. e. in the western
part of the old Finland), of whose prince bearing the family title of
Balder (not his given name) gets always his life companion and mother to
his children from amongst the Finnish speaking Vanir. The Vanir areas
being all the Finnish areas outside of South Finland, known collectively
by the names of Rosland and Karjala (i. e. the vast mass in geographic
and demographic sense being situated in the east).
The wife of Balder is a Van, or a Finnish speaking Finn, chosen from amongst the most beautiful women of all the various Vanir lands surrounding the land of the Aesir. The catch is, in this variant of the story, the so-called Balder upon the 27th birthday of his twelth son by a Van woman changes his family title from Balder to Per, or Väinämöinen in Finnish language. And anybody with even elementary knowledge of Nordic mythos knows that Väinämöinen is the Finnish name for Odin.
It's just the same narrative of western Odin marrying an eastern girl, of which Frisian, Scandinavian and Finnish variants we have just seen here.
The wife of Balder is a Van, or a Finnish speaking Finn, chosen from amongst the most beautiful women of all the various Vanir lands surrounding the land of the Aesir. The catch is, in this variant of the story, the so-called Balder upon the 27th birthday of his twelth son by a Van woman changes his family title from Balder to Per, or Väinämöinen in Finnish language. And anybody with even elementary knowledge of Nordic mythos knows that Väinämöinen is the Finnish name for Odin.
It's just the same narrative of western Odin marrying an eastern girl, of which Frisian, Scandinavian and Finnish variants we have just seen here.
FromFinland posted 04 January 2016 - 03:53 PM
Apol, on 04 January 2016 - 11:21 AM, said:
Boxströms had this to say on the topic, page 69 of the 1996 book:Everywhere where land has submerged or become flooded, it has been termed "Atlantis" - by laymen as well as scientists.
Lands that were covered
by ice during the Atlantis [ice age], have the 'land' in their names,
whereas tropical lands do not have such land-names. Lands under the ice
were Rosland [Russia], Vinland [Finland], Svealand, Daneland,
Frankenland, England and Holland, and for example Italy and Spain were
tropical. Thailand used to be called Siam.
Same book gives also altenate names for some of the nations above, such as Svearike for the Svealand and Danmark for the Daneland. The way I interpret this text and the book overall, is that it doesn't claim names like Frankenland, England or Holland to have been already in use by the end of the last ice age. It's more like that such naming system was applied in general in Nordic lands to such nations known to have been under the ice in the old times. The Boxströms claim that knowledge of ice age was known in the Nordic lands (including the later Medieval Christian period), which is not at all that odd to my mind, as a person visiting any Nordic nation can witness for himself/herself the levelling scraping-marks, that were left by the the receding ice blocks on the bedrock like everywhere.
We know from history books that in the Finnish language Finland's old names were such as Suomenmaa ('Land of Suomi') and Saarenmaa ('Land of Islands', today an island west of Estonian mainland). Likewise, Russia was either Venäjä in short form or Venäjänmaa in long form. Old Finnish administrative divisions from historical times also used plenty of the word 'land', as in Turunmaa ('land of Turku'), Hämeenmaa ('land of Häme'), Ahvenanmaa ('land of perch', or Åland) and so on.
FromFinland posted 04 January 2016 - 06:01 PM
Passing Time, on 04 January 2016 - 11:30 AM, said:
Yes and no. I'll explain: The Boxström family saga as presented by the Ior Bock has never been collected into one single book or documentary film, containing the whole saga in its entirety. Instead, there are several books by different authors, each of which tells something about the saga. The most comprehensive book on the subject was published only in the Finnish language in 1996. It is available online for ordering or from most of the larger Finnish libraries, classified either under 'non-Christian religion', 'mythology' or 'folk poetry'. To date it gives by far the best overview on the subject, altough even it doesn't include all the elements or components of the saga. It should be noted that it took 20 years to teach the entire saga to Ior Bock, so therefore it would be hard to contain all this huge amount of knowledge into a single book or tape recording.are the Boxstrom saga's available on line?
Since 1996 some information has been published in Finnish language by Ior's good friend and author Leo Nygren as several booklets of small distribution, some of them currently out of print. These books are likewise valuable as sources, though it's somewhat difficult to separate from their contents the Boxström traditions, Ior's personal opinions on matters or the authors personal opinions. This is not helped at all by the fact that mr. Nygren - while being a good man in person - doesn't have an academic background, with the result that IMHO his books can at times be easy to read, but at other times irritating as hell to read.
In 2010, before Ior's death he was interviewed, with some new details coming up.
In 1984 when Ior first spoke publicly about the matter, he was interviewed and the tape recordings catalogued and stored by the Finnish national authorities responsible for preserving the folklore, namely SKS and SLS. All the while during the 1980s, 1990s and 2000s Ior was subject to several televison appearances, some of which are as of 2016 available online: 1986, 1991 and 2002.
Finland's National Board of Antiquities has catalogued and commented on places relevant to the family tradition in question, but it has been seriously lacking in scope. The rocky Balder's temple of Sipoo is commented over there as "interesting from geological point of view", while if taken literally is true, but IMHO is an understatement of the century as per my own experience of that place. One doesn't need to believe the Boxström saga to see for oneself, that the place is seriously odd for a natural formation, including stone stairways for starters.
At the same time, Ior's personal friends from all over the planet made videos and audio records about the theme, some of which can be seen on the internet and some others were thought lost, but have been re-discovered recently in the 2010s. As all of this was a private hobby effort after the initial recordings of 1984, there was no central place where the information would be collected. North American Jim Chesnar has been the most active. He knew Ior personally in the 1980s and is able to relate the story in detail. His spelling of Finnish is better than his literary output, where he makes few small mistakes, which is understandable as he doesn't speak either Swedish or Finnish as his native language.
So to sum it up, the information is spread all over and large parts of it are only in Finnish or Swedish. If you're able to understand Swedish, Danish, Norwegian or Icelandic, this video from 1986 might be a good start.
Passing Time, on 04 January 2016 - 11:30 AM, said:
I'm not familiar with such a thing and couldn't find any relevant information by googling. Could you explain a little more, please? The ones I'm aware of are the Nordic male names of Thorfinn, Thor-like names of the Finnish royals (Thorri and Thora) and one of the Thor's many names Oku-Thor, that is Ukko-Thor from Finnish ukko 'old man' and ukkonen 'thunder'.could the name Finn's have anything to do with the constant mention of the INN , in many of the saga's where Thor is mentioned ?
Passing Time, on 04 January 2016 - 11:30 AM, said:
No, I haven't. I'm aware of the book thanks to this great forum thread. As I have currently several books to read, it may be realistic to say that I might not even be able to read it this year. It's contents sound interesting, though.have you ever read L.A.Waddell's The british Edda
Passing Time, on 04 January 2016 - 11:30 AM, said:
Sounds like the works of Laurence Gardner to my mind. As my interest is focused on the Northern European scene, I do not have much to say on these matters.where he seems to think that the stories of Thor, Odin and Balder are copies of older stories from probably Summerian times of Adam , Eve , Abel and Cain , re-named for the Eddas , and then re-named and re-worked again for the Arthurian Romances.........
Heer-Thor becoming Ar-Thor , Hother-us becoming Uther, Gewar King of Norway becoming Gewain , and his daughter
princess Nanna , being Arthurs Sister Anna , etc.. do you have any thoughts on this ?... regards PT
FromFinland posted 05 January 2016 - 03:37 PM
Passing Time, on 04 January 2016 - 11:22 PM, said:
Ah, now I see what you referred into. I had a quick look at The British Edda, and I say wow, that for sure is some deep stuff! Over there Inn is used in the connection of the Od, or Odin in the full long form, and Thor:regarding the mentions of the INN in the so called by Waddell.... The British Edda [...]
any idea what the Inn was , and if it could have any connection to the F-inns ?
Soul gave them Od(-am) o' the Inn (page 26)
Of all the dwarf tribes, and For Thor o ' the Inn, another. (page 47)
As I do not speak English as my first language, I had to check what the o' means and found out it means either of or on. Clearly Inn isn't here a reference to a hotel or a tavern. PT, I can see your point on it being a literary clue to the Finn or (F)Inn, as you would have it. Norse male name Thorfinn does indeed fit that pattern, as do some variants of the Norse mythos, where the heroes are from the Finnish cultural background. However, as the source of the text is (I guess) The Poetic Edda, I would first think of the possibility that it refers to Ing, as explained by authors of Wikipedia:
Ing was first amidst the East Danes
[...]
In Scandinavian mythology, Yngvi, alternatively spelled Yngve, was the progenitor of the Yngling lineage, a legendary dynasty of Swedish kings
[...]
The element Ing(o)- was widely used in Germanic names from an early period
For the Frisian connection, please have a look at the Wikipedia's take on the Ingaevones. In Finnish context we have the land area and tribal name of Inkeri, allegedly named after a Swedish princess living in the 11th century, though some see earlier 6th century Jordanes already referring to Inkeri as Inauxis.
My guess is on the Inn referring to the house of the Ing or Ynglinga, the premium Swedish royal family. So in my view the original text says in the modern English "Odin of the Ynglinga family" and "Thor of the Ynglinga family". As for Ell's take on the matter, I must confess I'm totally lost on what he refers into. Ell, could you open it up for me, please?
Posted 05 January 2016 - 06:08 PM
Abramelin, on 05 January 2016 - 05:15 PM, said:
How do you 'know'? Or better: why do you believe that?But I also know that Thiudiskland developed into Twiskland (Frisians) and Tyskland (Scandinavia), and it came into existence around the 12th century.
It can be the other way around, or the names can have existed simultaneously.
Quote
No, rather like Dütsk: Dütsch: Deutsch.in Westphalia they say Düsk instead of Deutsch. Sounds an awful lot like Twisk or Tysk, don't you think?
Quote
Neither is it in the OLB.Nowhere before the 12th century is Germany called Thiudiskland
Posted 06 January 2016 - 11:31 AM
Othar, on 05 January 2016 - 06:13 PM, said:
Numbers added by me:Apol, did you notice that the ode to Frya ("Frya was white like snow ...") has twelve parts too?
1 FRYA
WAS WIT LIK SNÉI BY.T MÔRNE.RÁD
ÀND THAT BLÁW HJRAR ÔGNUM.
WN.ET JETA THÉRE RÉINBÔGE OF.
2 SKÉNE FRYA.
LIK STRÉLON THÉRE MIDDÉI SVNNE
BLIKADON HJRA HÉRON THÉR SA FIN WÉRON AS RACH.
3 ÁBÉLE.FRYA.
VNTLVKTON HJRA WÉRA.
THAN SWÉGON THA FÜGELON
ÀND NE RORDON THA BLÉDAR NAVT MAR.
4 WELDIGE.FRYA.
THRVCH THENE KRÀFT HJRAR BLIKKAR
STRÉK THENE LÁWA TOFARA HJARA FYT DÀL
ÀND HELD THENE ADDUR SIN GIF TOBÀK.
5 RÉNE FRYA.
HJRA YTA WAS HÜNING ÀND HIRA DRANK WAS DÁWA.
GÁDÛRAD ANDA BÒSMA THÉRA BLOMMUN.
6 LICHTE FRYA.
THÀT FORMA HWAT HJU HIRA BÀRN LÉRDE WAS SELV.TWANG.
THÀT ÔTHERA WAS LÍAFTE TO DÜGED.
ÀND THÁ HJA JÉROCH WRDON.
THÁ LÉRDE HJU HJAM THJU WÉRTHA FON THA FRYDOM KÀNNA.
HWAND SÉIDE HJU.
SVNDER FRYDOM SEND ALLE ÔTHERA DÜGEDON.
ALLÉNA GOD VMBE JO TO SLÁVONA TO MAKJANDE.
JVWE OFKVMSTE TO ÉVGE SKANTHA.
7 MILDE FRYA.
NÀMMER LÍT HJU MÉT.AL UT JRTHA DÀLVA VMB ÀJN.BÁT.
MEN SAHWERSA HJU.T DÉDE. WÉRE.T TO JAHWELIKIS NOT.
8 LUKIGOSTE FRYA.
ALSA THA STÀRA OM JRTHA OM.SWÍRMJA
SWIRMDON HIARA BÀRN OM HJA.
9 WISE FRYA.
THA HJU HIRA BÀRN VPBROCHT HÉDE
ALTO THÉRE SJUGONDE KNY.
THÁ HROP HJU.RA ALLE A FLÍLÁND TO SÁMNE.
THÉR JEF SE HJAM HIRA TEX. ÀND SÉIDE.
LÉT THAM JVWE WÉI.WISAR WÉSA.
THA NE SKIL THÀT JO NÁ NAVT KWALIK NI GÁ.
10 UT.FOR.KÉRENA FRYA.
THÁ HJU SÉID HÉDE. BÉVADE JRTHA LÎK WR.ALDA.S SÉ.
FLÍLÁNDIS BODEM SVNK AN.GRÁDA VNDER HJARA FYT DÀL.
THJU LÒFT WÀRT SWART ÀND NÍ LOF FON TÁRA TO STIRTANE
ÀND THÁ HJA NÉI MODER OM.SÁGON
WAS HJU AL.LANG VPRIRA WÁKSTÀR.
THA TO THA LESTA SPRÀK TÒNGAR UT.A WÒLKA
ÀND BLIXEN SKRÉF AN.THÀT LÒFT.RVM.. WÁK.
11 FAR.SJANDA.FRYA.
THÀT LÁND FON HWÉR HJU WAS VPFÁREN WAS NW EN STRÁM.
ÀND BUTA HIRA TEX WAS THÉR.IN ELLA BIDVLWEN
HWAT FON HJRA HÔNDUM KÉMEN WAS.
12 HÉRIGA.BÀRN.
THA HJA TO.RA SELVA WÉRON.
THA MÁKADON HJA THIT HÁGE THERP
BVWADON THÁS BURCH THÉR VPPA.
ANDA WÀGRUM THESSA WRYTON HJA THENE TEX.
ÀND VMBE THAT ALLERA MANNALIK HJA SKOLDE MÜGA FINDA
HÀVATH HJA THÀT LAND RONDOMME TEX.LAND HÉTEN.
THÉRVMBE SKIL.ÀT BILÍWA ALWENNE JRTHA. JRTHA SÍ.
Posted 08 January 2016 - 10:58 AM
Apol, on 08 January 2016 - 09:07 AM, said:
Nice, I had not noticed yet. I do not think it is just a coincidence.Did you know that there are 12 femme-burghs in Freyjasland - according to page 5?
BTW the Netherlands currently has 12 provinces...
Posted 08 January 2016 - 08:44 PM
Abramelin, on 08 January 2016 - 06:29 PM, said:
These threads have countless examples of failing 'official' etymology and I have seen many cases of etymologists disagreeing on fundamental questions among each other.This is the etymological dictionary I used...
The dictionary you used assumes that "tiusche (lant)" is derived from "theodisca" (and varieties), but provides no evidence or arguments.
edit to add: But even if it had provided evidence for this, it would not have proven that "TWISKLAND" could not (also) have been an ancient name.
Quote
Don't imagine you know what I think or (don't) want. We've been there. Let's stick to the facts.You just don't want to see...
Quote
Things may be odd in your perception, but that does not make them impossible.And it would be somewhat odd...
This is not a scientific approach.
As always until now, your argument boils down to "I just can't imagine that the OLB is authentic."
Many discoveries in the past could not be imagined by 'skeptics' until they were generally accepted (and 'obviously' true).
Posted 08 January 2016 - 08:50 PM
Abramelin, on 08 January 2016 - 06:53 PM, said:
Page 1: THET BOK THÉRA Á.DEL.A.FOLSTAR.... the name of the book is actually inside the OLB:
...et bok thêra Adellinga
page 91: THET BOK THÉRA ADELA FOLLISTAR
But all three names do not refer to the 'final' version, incl. (a.o.) the text about Black Adel and the letters by Hidde and Liko.
So Ottema's use of another name is justified.
Posted 09 January 2016 - 10:27 AM
Apol, on 09 January 2016 - 09:08 AM, said:
Excellent.... in Hjalmar Falk and Alf Torp's Norwegian/Danish etymological dictionary, Etymologisk Ordbog over det Norske og det Danske Sprog (1903-06 / 2006), we find the word tyskendæk, which is borrowed from Dutch tusschendek (of a ship).
tysk - twisk - tusschen
This makes "twiskland" an argument in favour of OLB's authenticity.
Tusen takk, Apol!
Apol posted 13 January 2016 - 11:10 AM
Othar, on 10 January 2016 - 02:46 PM, said:
This is strange. I wasn't able to find again the book I downloaded a couple of days ago. It seems like it has been removed from visibility.Could be very interesting, but link does not seem to work and I can't find the book online. Can you check please?
But, luckily, I found another edition (Andreas Duncker, Brunswick, 1656):
https://books.google...dvardvs&f=false
"Themis Hyperborea, siue de Tabvla Regvm Frisiæ" is on page 729
FromFinland posted 14 January 2016 - 11:24 PM
Othar said:
The book chapter linked by Apol mentions Zealand of Denmark and the East and West Götaland of southern Sweden. Perhaps this Beowulfian landscape is the home of the "High-Nordic peoples"?Joachim Hoppers (1523-1576) was a Frisian lawyer and professor who worked for the Spanish king (Philip II). He appears to have written about Frisia's ancient history, but I have not found that text yet. According to the "Chronique", he wrote that the Frisians stem from the "High-Nordic peoples or Hyperboreans" and were the first to have received the secrets of writing.
Edit: in the Boxström family saga it's the Dan (of three brothers Sven, Dan and Fin), who moves to Denmark to establish a dynasty, that in turn fathers all the continental Nordic white peoples of Central Europe (i. e. Frisians, Angles, Saxons, Franks and such). As a source it emphasises how the Central European heathen dynasties are all off-shoots of the Danish line, unlike the people of the Scandinavian Peninsula (Sven's people) and East Europe (Fin's people).
FromFinland posted 15 January 2016 - 04:01 PM
Ell, on 15 January 2016 - 12:24 AM, said:
The Finnish variant of the brother story beautifully entwines three stories known from other sources:I also suspect Sven, Dan and Fin to be identical with the Vé, Odin and Vili of Asgardian mythology.
1. Story of Dan and Angul, founders of Denmark and England, as related by Saxo Grammaticus.
2. Story of Fornjótr the ruler of Gotland, Finland and Kvenland, for Sven, Dan and Fin were too from Gotland originally, before spreading out to found Nordic nations.
3 The story of Gutasaga. Attention Frisian readers: note the Greek connection over there!
It's good you Ell noticed the similarity to the Odin brotherhood of Vé, Odin and Vili, and I must add here that the Austro-Hungarian Wiligut family tradition, as relayed by officer Karl Maria Wiligut (1866-1946), claimed descent from the Vili branch, whereas the Finnish Boxström family tradition claims descent from the Fin branch.
Othar, on 15 January 2016 - 03:27 PM, said:
Perhaps you wrote in a rhetorical sense, but merely glancing at the pages one sees that vast majority of the pages in question do not speak of geographical or demographical matters. Some pages seem to have something about Roman gods, and finally on the page 741 we have suddenly three real-life Nordic place names in succession. Page 741 is the right one, if you ask me.I would not know where to start
Abramelin posted 16 January 2016 - 04:48 PM
I remember we disussed the word "bukja" not that long ago, but I only get search results from the 2nd part of this thread.Anyway, everyone here was convinced that the translation should be "girl" or "little girl", based on "buik" = belly, and so on.
I , however, am convinced it should be translated into "little boy".
This the passage from the OLB:
[MS73]
As Sêkrops sach (...)
Friesch Woordenboek- Lexicon Frisicum (started by Halbertsma):
page 212 of the book, page 240 of the online pdf:
boike: dim.n. jongetje, knaapje. Vgl. (Wieringer) baike, kind. Kex. 429. (EN: little boy, lad)
page 244 of the book, page 272 of online pdf:
bûke (with an accent circonflex on top of the -u-): voc. jongetje, maatje (EN: little boy, mate, or matie (?))
https://archive.org/...rdenb01horngoog
In short: the Lexicon gives us words (boike & bûke) that come very close to the OLB "bukja".
And watching a movie ("Elysium", a scifi movie with Jodie Foster and Matt Damon) recently, I heard a South African, the 'bad guy' called 'Kruger' (played by Sharlto Copley), say the word "boykie" a couple of times, when he and Matt Demon were beating the crap out of each other, and Matt Demon - for those who don't know him - is not a girl, lol. An interesting aside: one of the main characters in this movie, a woman, is called "Frey".
"Where are you, boykie? Where are you?"
"Eh, boykie?"
"You've got some fire in you, boykie."
And in the English subtitles the word "boykie" is not translated, and in italics (which is odd, because the producers were also South Africans).
South Afrikaans has retained a lot of archaic features of the Dutch language.
FromFinland posted 17 January 2016 - 01:50 PM
Tony S., on 28 December 2015 - 12:51 PM, said:
Here's alternative etymology for the Magy: in Finnish language mahti means 'might', but also on spiritual sense. Mr. Raimo Jussila, a licentiate of philosophy, has the following to tell in his dictionary book Kalevalan sanakirja (Otava 2009), page 213:The priests are the only rulers; they call themselves Magyars, and their headman Magy. He is high priest and king in one. The rest of the people are of no account, and in subjection to them. This people have not even a name; but we call them Finns, because although all the festivals are melancholy and bloody, they are so formal that we are inferior to them in that respect. But still they are not to be envied, because they are slaves to their priests, and still more to their creeds. They believe that evil spirits abound everywhere, and enter into men and beasts, but of Wr-alda’s spirit they know nothing. The Magyars affirm that they can exorcise and recall the evil spirits, and this frightens the people, so that you never see a cheerful face.
- mahti [lit. 'might'] 1. ability to cast spells, ability to do magic [...]
- mahtimies [lit. 'man of might'] a sage, a wizard [...]
- mahtipontinen [lit. 'mighty'] one who knows mighty spells
Of course, it could just be a variant of the tribal name Magyar, in a bit similar way how a leader of a Germanic Hundertschaft was called Hunno, a dual status both for a civilian and military roles (as per the page 25 of J. O. Hannula's 1931 book Sotataidon Historia II).
FromFinland posted 17 January 2016 - 05:03 PM
As for whether Oera Linda book's Finns have any relations to the Nordic Finns, let see what Julius Krohn
had to tell in his book 'The heathen service of the Finnish kin'
(Finnish Literature Society, Helsinki, 1984, pages 35, 124-126, my
translations):
Everytime one went to
take a bath [at the lake], one had to take grain to the big stone of
Immonen. [...] Kirsti Toivanen had been for long the priestess of the
stone; through her the offers were laid and she told the people doing
the sacrifice the answers given by the elves. On the eastern beach of
the Vahvajärvi at Tikanmäki had been similar offering stone. When it's
priestess, the old hag, passed away the stone broke into several pieces.
In year 1534 arch-bishop Makarij, as has been mentioned earlier, complains that the tschudes [ethnic Finns] living in the Novgorod area have their own priests, which are called 'ballot casters' [arpojat], arbui, of whose chapels they bought sacrifices.
On one different
occasion, the Estonians cast a lot between a fat ox and just as fat
[Christian] priest, which they had seated on the ox's back. It's not
told in detail how it actually happened, only that the lot was cast on
the ox, which was immediately butchered. Possibly the same people's
elders who held the offer, also acted as warchiefs during a war, and as
judges during the peace.
Still in these days
[1894] there has remained recollections of sacrificial priests. To
Russwurm had one man in the Mihkeli parish of western Estonia told, that
he had once seen his grandfather to kneel down before a great stone
lying in a field. When he had inquired, what his grandpa was up to, the
grandpa slammed his hand on his ears and told to keep silent on the
matter, yet declared at the same, that they were descendants of a priest
family, of whose holy duty was to serve the old gods.
Of Estonian wise men, targad [tark = 'wise', tarkka = 'precise', 'sharp'], exists notes worthy of attention. According to Wiedemann they existed in different types: salt-targad or salt-speakers, word-targad or pronouncers, wind- and stone-targad, of which the latter were able to explain the lines in the chalk stone, and the mightiest of all, the so-called Mana-targad [Manala = 'underworld'].
Of Finnish sacrificial
priests hardly anything is know for the simple reason, that common
sacrifices have almost disappeared, save for eastern Carelia or Russian
side [of the border]. As we have discussed earlier of those female
priests, who in Leppälahti took the sacrifices, for other people too, to
the holy stones and told them the answers given by the elves.
As for the "but, like the Egyptians, they have priests and also statues in their churches", let's have Kaarle Krohn speak on the subject in his book 'Religions of the Finnish kin' (Helsinki 1915, page 209, my translation):
In the Estonia proper's famous sacrificial grove it's told of the missionaries to have felled "the made images and such ones".
In [Estonian island of] Saarenmaa it's mentioned that the [Christian] Germans upon conquering one castle threw out the picture depicting Tarapitha, or Thor.
The statues of Finn's are well known is Nordic sagas, which detail the adventures in the Finnish Bjarmaland or Risaland (Rysland, or Russia). There the Finns have rich statues for so-called Jomali, which means in Finnish 'god' (jumala). As told in the occasionally high-fantastic saga of Bosi and Heraud:
Here in the forest
stands a great temple. King Harek owns it, who rules here over
Bjarmaland. The god called Jomali is worshipped. There is much gold and
treasure. The king's mother, who is called Kolfrosta, is in charge of
the temple.
[...]
They came to the altar
where Jomali was sitting. They took the gold crown from him, set with
twelve gemstones, and a necklace, worth three hundred gold marks, and
from his knees they took a silver cup so large, that even four men could
not empty it. It was full of red gold. But the precious canopy, which
hung over Jomala, was worth more than the contents of three ships, the
richest to sail the Mediterranean Sea. They took it all for themselves.
Same statue of Jomali existed in 1026 A.D. when the historical person Torer Hund visited it in Bjarmaland. It's described as being of propably wooden make and situationed in a wooden grove. It had a thick and valuable neck chain and at it's knees it had a silver bowl full of money. In addition the same garden-grove had a burial mound full of treasures and was guarded by six guards at all times.
Apol, on 17 January 2016 - 02:31 PM, said:
While being a minor detail to the matter you write of, I must here relate that according to Jordanes the Gothic king Tanausis beat the pharaoh Vesosis' attack in the battle of river Phasis of modern-day Georgia. Name of the pharaoh Vesosis, or Sesostris, is believed to refer to Senusret III, who is in turn though to have reigned from 1878 BC to 1839 BC.It was certainly Ahmose I who was the pharaoh in 1551 BC. [...] No pharaoh had made military campaigns that far north in the Levant before.
Jordanes claims to base his knowledge on written sources:
For myself, I prefer to believe what I have read, rather than put trust in old wives' tales.
FromFinland posted 18 January 2016 - 06:50 PM
Abramelin, on 18 January 2016 - 04:35 PM, said:
Maybe, but on the other hand a 'boy' is pojke in Swedish (as Ell told) and poika in Finnish. As words and names tend to become shorter in time, one would suspect for the long form to be the one of a great age.*Here it says that "boykie" comes from English "boy", and that the 'kie' ending is the S-African diminutive: https://en.wikipedia...nglish_coinages
The diminutive ending might still apply, as in flicka or 'girl', as opposed to the adult man/kvinna, which do not have the ykie/jke/ika-ending. (k -> youngster, n -> adult.)
(made bold by me, Othar:)
*Yes, I know the so-called linguists have their *PIE fantasies of the
exact opposite lineage, where *asterix words are invented to back up
made-up theories and the southern European known variants of the words
are always considered to be as of more ancient age, as if they were
somehow immune to the vast cultural changes known to have happened over
there. Totally unlike the Nordic part of the Europe, which has had
relatively little known genetical or cultural change since the end of
the last ice-age, and thus IMHO likely retains the most archaic worlds
still in use in the whole Europe.
FromFinland posted 20 January 2016 - 04:47 PM
Ell, on 20 January 2016 - 10:59 AM, said:
I agree with the folk etymology. Interestingly it's a Nordic variant of the international theme. Wikipedia shares the Greco-Roman view, my bolding:Alfabet is also the Dutch spelling. Generally the word is considered to be composed of the names of the first two letters in the alphabet, so I would not attach too much value to alfernas beten: it appears to be a bit of folk etymology. And might 'beten' perchance be related to the English 'bit' instead? Little bits of spoken or written language?
Plutarch, in Moralia,
presents a discussion on why the letter alpha stands first in the
alphabet. Ammonius asks Plutarch what he, being a Boeotian, has to say
for Cadmus, the Phoenician who reputedly settled in Thebes and
introduced the alphabet to Greece, placing alpha first because it is the Phoenician name for ox
— which, unlike Hesiod, the Phoenicians considered not the second or
third, but the first of all necessities. "Nothing at all," Plutarch
replied. He then added that he would rather be assisted by Lamprias, his
own grandfather, than by Dionysus' grandfather, i.e. Cadmus. For
Lamprias had said that the first articulate sound made is "alpha", because it is very plain and simple — the air coming off the mouth does not require any motion of the tongue — and therefore this is the first sound that children make.
In the Boxström saga, it's the A B C D ..., so it's the second sound after A. They make alfernas beten, and the word alfer ('elves') is said to come from alla fer, or 'all cattle' (fä in modern Swedish). It's represented as heathen folk faith in a good custodian spirit that takes care of the household and cattle, especially during the winter time. So it's more or less the same cattle etymology as the Phoenician ox etymology. Interestingly, the bi-lingual Boxström saga also claims that first human being Frei (or Sampo on Finnish) was able to speak primaeval Nordic language (of A B C D E F ...) naturally and genetically, and teached it to his sister Freia (or Aino in Finnish) at the age of seven years:
"The language of Sampo was based on the human's natural sounds, which are created at the brains of all human beings." (Bock 1996, page 17, my translation.)
So, the Boxström saga in this respect has also the Plutarch's take included within it. It will be interesting to see what the Frisian take is on the matter. While it's common nowadays to think the North Europeans learned the current system from Latin of the Medieval Christians, there's evidence for a similar writing system being used in Europe at far more older times.
German bitte (and English please) might be connected to beten, as it's polite and socially conforming to say so.
Tony S., on 20 January 2016 - 01:25 AM, said:
Not an exact match, but something a bit similar is found in the Boxström saga, where the aesir royals had a very special kind of stone tower. The first floor had five corners, second floor had six corners, third floor had seven corners and so on. I believe this refers to the inside corners and that the outside wall was apparently circular in this legend. Allegedly remnants of this tower architecture can be seen also in the towers of the later historical times, namely those of the Raseborg and Olavinlinna castles. This odd fractal-like architecture is claimed to be a superbly resilient structural form, so it would be interesting to get a real construction engineers opinion on it. One 'bell-tower' is detailed as covered in white chalk and one other as "golden", or covered by countless small gold sheets. All of these were allegedly demolished in 1050 A.D., followed by sinking of the construction stones to the nearby sea by the spring of 1051 A.D.How do we envisage the lamp, or foddik, "hanging" in the tower, and the configuration of the tower itself and its six walls?
Posted 21 January 2016 - 09:36 AM
Van Gorp, on 21 January 2016 - 03:06 AM, said:
Athe could be translated as friend, but in my opinion allie (bondgenoot) is more accurate and fit every where it is used.For me the consensus goes as far as Salt-Athe carries the litteral meaning of Salt and Friend...
There is at least one example where ATHA and FRJUNDA are both mentioned, indicating that the words had different meanings.
page 26, point 7
TILTHJU WI ÁTHA ÀND FRJUNDA WINNA
in order for us to win allies and friends
It is also noteworthy that besides SALTATHA the term WÉRAR (defenders) is used. These people were not paid and seen as more honorable, since they did not fight for money, but for their land and their folk.
Posted 22 January 2016 - 09:11 PM
Abramelin, on 22 January 2016 - 07:47 PM, said:
Not all that many documents from before that, are there?Let me guess: Tyskland showed up in Sweden, Denmark and Norway....after the 12th century.
And it may have been one of various spoken names before it became the main written name.
Posted 24 January 2016 - 10:12 AM
Ell, on 20 January 2016 - 11:16 AM, said:
Page 206, line 1, about the Frya's Burgh at Texland, during the reign of king Askar, that is shortly before our year zero:I also wonder about the walls themselves: were they stone walls or wooden walls? If stone, archaeological remains might be found. But I rather suspect / feel that the walls were made from wood.
NACHTIS WRDON THA FÁMNA UT.ÉRE BURCH DRÍWEN
ÀND OGTIN.S KVN MÀN FON THÉRE BURCH ALLÉNA ÉNE GLANDERE HÁPE SJAN.
At night the maidens were driven out of the burgh
and in the morning only a glowing heap was left of it.
(literally: ...one could only see a glowing heap of the burgh.)
So at least the main burgh was made of wood (and other materials that burn or melt), even in the most recent of described (in OLB) times.
(Apollania's burgh in Ljudgárda was made of baked bricks.)
(...) Anyway, the argument that a lack of archaeological remains would disprove OLB's authenticity is invalid.
As I have pointed out before, there are historical sources of there having been (in the 13th century) a castle of the Dutch counts in the Westfrisian village where I grew up, yet no remains of it have ever been found (so far). Oral tradition is (as far as I remember), that the villagers had hated it so much, that they took it apart to the last stone.
But as for the 'Fryan' burghs, other explanations are also possible.
As I have pointed out before, there are historical sources of there having been (in the 13th century) a castle of the Dutch counts in the Westfrisian village where I grew up, yet no remains of it have ever been found (so far). Oral tradition is (as far as I remember), that the villagers had hated it so much, that they took it apart to the last stone.
But as for the 'Fryan' burghs, other explanations are also possible.
Posted 24 January 2016 - 09:43 PM
BTW Tony, I have seen many JOL-like windows in Friesland, for example this former church in Pingjum:
FromFinland posted 26 January 2016 - 10:38 AM
As for the holy fire of Van Gorp and Passing Time, let's see what Austro-Hungarian officer Karl Maria Wiligut (1866-1946) had to say on his family traditions, writing in 1935:So, would they be more like the brochs or wheelhouses then?Given that the tower is 90 feet tall, which is only slightly more than twice 42, we should not be imagining a tall, thin tower at all, but actually a rather low, wide one. If the sides were more than 21 feet wide (they cannot possibly be less, given the position of the attached houses), this wideness is increased still further.
The institution of girls' schools developed out of the extremely ancient "Modranekth."2 [2
"society of maidens"] [...] So, for example, it came about that virgins
who were chosen as BURGMAIDENS had to conform special conditions. [...]
The corps of maidens
was organized in four groups, which are: The lowest group, the HEXAS
[witches], had as their duty the care and preservation of the eternal
flame and its kindling for purposes of signaling (by day with smoke, by
night with a bright flame)[*]. Fire was fetched from these women as a
part of certain ceremonies or ritual (Ara-Ryta] for the lighting the
hearth-fire of newly married couples. As a part of land-taking or new
settlement ceremonies, or when perhaps the hearth-fire had gone out,
fire was kindled from live coals from these eternal fires. The Hexas
were initiated into herbology in some tribes and communities in addition
to their service relevan to the fire. [...]
From this presentation of the basic division of the Maidenschaft
it is clear what a deep meaning the position of women had in past
times. In the clan she was the protector and irector of honor of men as
well as women. In the tribe she was the representative of high
idealistic flights of thought and the kindler of enthuasism for great
aims in the interest of the tribe and folk. [...]
Closely connected to
the cosmos, to the All and to God, and reflecting the rhytmic lwas of
these in her soul, she was the bearer of the whole of our tradition in
our prehistoric past. It was with this understanding that the education
of the female youth was designed. [The Secret King, translated by Stephen Flowers, 2001.]
* Such signaling reminds not only of the beacon ligh houses for the sailors, but also of the Finnish hill fort system, where they were situated according to archeologists so that they could alarm each other by signal fire and smoke. This is seen in the story of Norwegian Saint Olaf, where he attacks Finnish coast called Balegard (as in English 'balefire' or Finnish palo 'fire'), yet the heathen Finns succesfully evade him by withdrawing to inland, and then after amassing their own forces make a counter-attack. This all means that they likely had a foreknowledge of the impeding raid, as the counter actions had been systematic and not haphazard or random in style. Thus also the Wiligut story of signal fire makes sense in the North European cultural context.
Apol said:
I don't know about you Scandinavians, but here in Finland we have this thing called joululyhty. In the primary school we all children made ones. While they nowadays are any lamps with small candles inside, the iconography of the German julleuchter (hearts, wheels, zigzag) is well known from folk wood art of all Nordic nations, including ours.In fact, I tend to believe that the Lamp must have been something like the ancient so-called 'julleuchters', which have been found in different places in Northern Europe
Posted 26 January 2016 - 07:46 PM
Tony S., on 26 January 2016 - 06:48 PM, said:
A well known contemporary referred to Wralda (quoted in various spellings) on several occasions (translated from German and selfsensored to avoid ban):Do you have other quotes from any of his contemporaries that reference the OLB?
"Who observes and understands the process of selection in nature, is at the core a believer (in a higher power). He is a believer, because he knows there is an endlessly wise sovereignty above us. The ancient Germans had a beautiful expression for that: Waralda; the most ancient." (date unknown)
"Atheism is the only world, or religious view that is not tolerated within the [censored] [...] I have not tolerated an atheist in the ranks of the [censored]. Every member has a deep faith in God, in what my ancestors called in their language Waralda, the ancient one, the one who is mightier than we are." (date unknown)
(1942): "Today at [censored] funeral I intentionally expressed in my oration from my deepest conviction a belief in God, a belief in fate, in the ancient one as I called him - that is the old Germanic word: Wralda."
(1943): "... above us is an infinite wisdom. The Teutons had a beautiful expression for it: Waralda, the ancient. We may dispute how it can be revered and how in earthly terms it can be broken down into cults and varieties."
(1945): "The Most-Ancient ("Uralte") will protect us and particularly the brave/ good German people, and not let us perish."
FromFinland posted 26 January 2016 - 09:12 PM
Tony S., on 26 January 2016 - 06:48 PM, said:
No, unfortunately. Have you read Stephen Flower's English translation published in 2001? If you have not, please do. In my humble opinion, OLB addicts out here should check the Wiligut stuff, too!Do you have other quotes from any of his contemporaries that reference the OLB?
While the Wiligut stuff has thematic similarities to OLB, the overwhelming majority of the content is very different in nature. Same words more or less describe also the link between the Wiligut and Boxström family sagas: similar, but not an exact match. There is a very good reason to believe, that at least the connection between the two later sources may not have been due to purposeful copying, for there existed a significant time gap of 17 years between their availability here in Finland. And frankly, I doubt that the Wiligut stuff was much known before the 2000s or Internet in the West Europe, either. While the name and personality of mr. Wiligut perhaps were, along with the Wewelsburg castle, the pre-historic contents of his writings and articles do not seem to have been well known at all.
Posted 26 January 2016 - 09:15 PM
Tony S., on 26 January 2016 - 07:59 PM, said:
At least that... what else do we know about him that justifies the assertion that is sometimes given that the OLB was his "bible"?
1) he had the OLB secretely researched until 1943 and
2) that in 1942 he had planned to have a splendor-edition made to give to his "leader" as a present, but this was cancelled after the latter had made a speech that was not favorable of things related to Atlantis research.
(I can be more specific tomorrow, when I am in my library.)
A German emeritus scholar who collected almost all there is to collect about this, offered to share his sources with me, but I won't have time to indulge in them in the near future.
I also know now that one of the main reasons to publicly reject OLB as authentic in '34 was, that it was politically inconvenient, because it would suggest that "Slavic" peoples had already since ancient times lived in areas that they wanted to claim for Germanics. This would have been enough reason to delay admitting authenticity till after the war.
FromFinland posted 26 January 2016 - 09:41 PM
I'm aware of this anonymous "leader" having made a public speech where
he riciduled all those looking for ancient Germanic things for guidance.
To my knowledge, this "leader" was of a future-oriented type, and for
him the ancient pre-history had been a springboard to modern times, not a
great thing in itself. He for example considered the Greco-Roman
influence in the arts an integral part of modern European identity,
which could indeed be seen very well in the WW2 architecture of the
"must-not-be-named"-land.
Passing Time, on 26 January 2016 - 10:07 PM, said:
Sure! The Secret King, Karl Maria Wiligut, Himmler's Lord of Runes. Translated by Stephen E. Flowers. Published by Dominion / Rûna-Raven, 2001.have you got a title for the wiligut book/s , and are they available in english?
As per the page 99, mr. Wiligut claimed that his family story were allegedly carved in wooden boards in "linear script", which along with other family documents perished in a 1848 fire in Ofen, or Buda today.
Some parts of the Wiligut story seem to be influenced Christian and later historical times, which I also myself see in the the Boxtröm family saga. This is not at all odd, for Germanic Christianity has roots stretching to the antiquity. The 2001 book is important also for the 1997 interview of the Gabriele Winkler-Dechend, which it contains. Lady Winkler-Dechend (1908-?) knew mr. Wiligut personally and in addition to providing some additional information also shoots down some unfounded rumours, such as that mr. Wiligut allegedly had some parapsychological abilities.
Also this is a good place to inform the English readeship here, that Ior Bock of the Boxström saga fame was asked in 2010 whether he was aware of the Wiligut story, for it contains few peculiar similarities. The answer was no, which is to my mind believable, based on what we know both of mr. Bock's reading habits and his interests in general.
FromFinland posted 27 January 2016 - 04:16 PM
Tony S., on 27 January 2016 - 02:06 PM, said:
In traditional Finnish, juutti means 'a Dane'. Pages 53-54 of J.R.R. Tolkien's Finn and Hengest (HarperCollins 1990) tell it could be also written eotena or eoten. Kristfrid Ganander, writing in 1789, has the Joter refer to Finns of the olden days. For more information, please see Fornjót, Oium, Reidgotaland, Jordanes and - interestingly - Gutians.The Gutones were almost certainly the Jutes, of Jutland, and jute is another word for amber. The Jutes, of course, are called the Juttar in the OLB. They later migrated to England and settled in Kent, Hampshire and the Isle of Wight.
Tony S. said:
Tony, your website has been helpful for me when I study the OLB. I like very much that you have not only put up the text online over there, but have also put some though on the visuals (maps, fonts, colours) as well. Its great we have not just one, but many sites (yours, Apol's, Othar's, Abramelin's) that look at OLB from different points of view. And if one of them goes offline for reason or another, we still have the information available on somebody's website. Unfortunately this is not at all the case with many other sources.please feel free to have a look at my website in my sig
I have this pipe dream, that maybe someday we Europeans would have one website portal to a database, that would include all such sources plus Tacitus, Caesar, Monmouth, sagas etc. in an easy to use web interface, where one could see the original and the English translations side by side. This would be of great help for students, hobbyists, professional researchers and all. It would also include such texts that may or may not be modern fabrications (like Hrafnagaldur Ódins, Book of Veles, Kolbrin bible etc.), for one man's forgery is another's Bible, and we should not limit information flow, just because of what we think to be authentic. The largest obstacles is see now are possible copyright issues, which is a shame as in the old European culture sharing is caring was very much the normal attitude in research and studies.
Apol posted 27 January 2016 - 04:19 PM
Here is a corrected map of the burg of Ljudgârda: